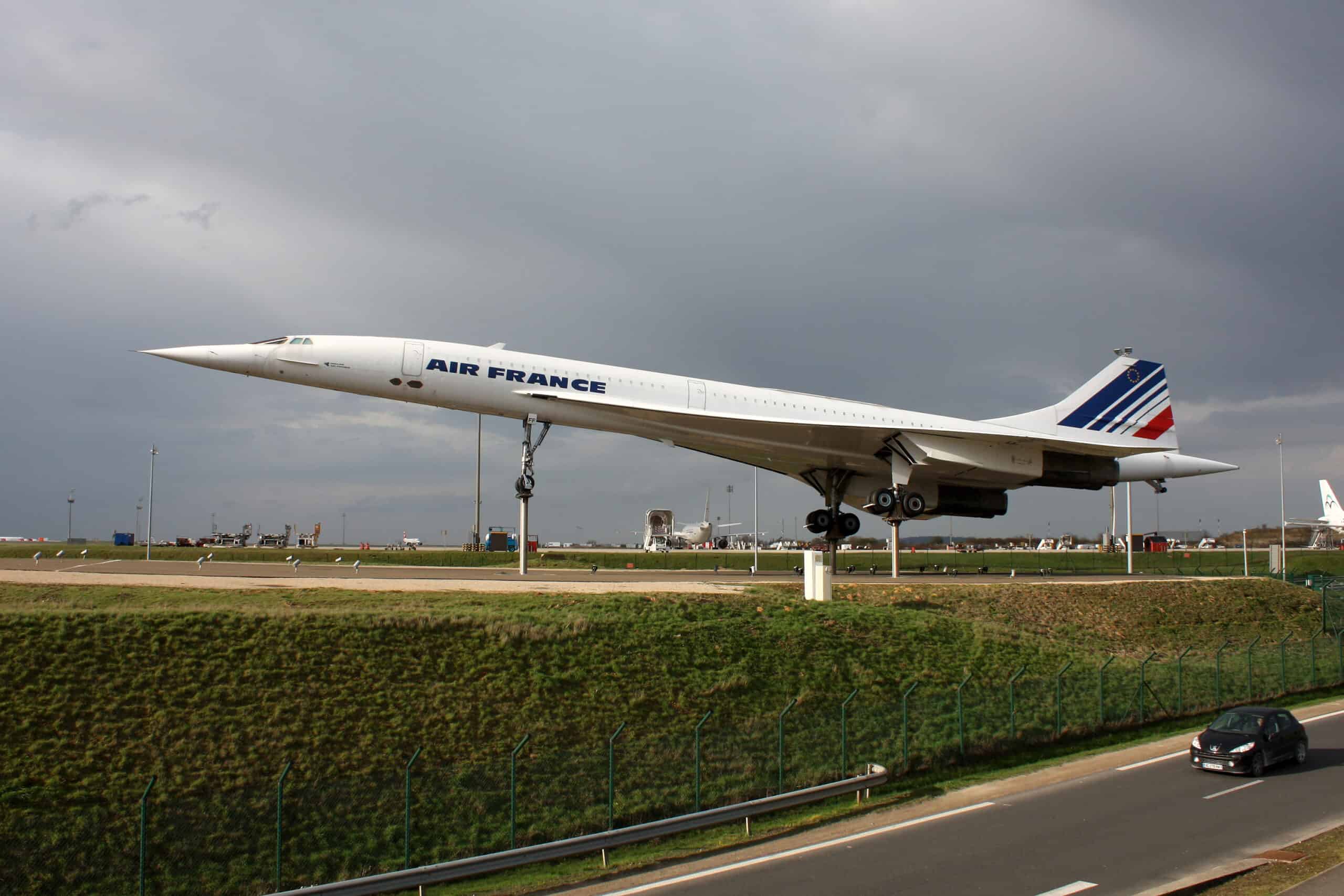
The Supersonic Concorde was a commercial passenger aircraft developed in a joint partnership between the British and French governments. The aircraft was considered a breakthrough invention in air travel as it flew at twice the speed of sound.
However, the plane was short-lived as it ceased operations in 2003, 27 years after it began its commercial operations in 1976. This article will examine the Supersonic Concorde’s failure, including its history and why the aircraft was permanently grounded.
Let’s get to it!
Quick Facts
| Launched | 1969 |
| First Commercial Flight | 1976 |
| Retired | 2003 |
| Top Speed | 2,179 km/h |
| Engine Type | Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 |
| Passenger Capacity | 128 |

©By Plismo – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6797020 – Original / License
Supersonic Concorde History: What to Know
The Supersonic Concorde was the first major joint venture between European countries to design and build an aircraft. The plan was conceived in 1962 when Britain and France signed a treaty to share costs and liabilities in developing supersonic transport.
British Aerospace and a French company known as Aerospatiale were tasked with designing the aircraft, while Rolls-Royce and SNECMA from France were tasked with constructing the jet engines.
The result of the planned ventures was a technological masterpiece: the Concorde, whose development ended in 1969 as the aircraft made its first flight. In the 21st Century, the magnitude of the Supersonic Concorde’s invention can only be compared to SpaceX.
The powerful jet engine transformed air travel, giving the aircraft a maximum cruising speed of 1,354 miles (2,179 km) per hour (this is still less than half the speed of rockets). The incredible speed significantly reduced travel time as the journey from London to New York was reduced to a three-hour flight.
Developing the Supersonic Concorde undoubtedly showcased European governments’ and manufacturers’ potential when cooperating in ventures. Similarly, it cemented Europe’s place at the forefront of aerospace development. However, building the Supersonic Concorde was quite expensive, and the development cost could not be fully recovered from the airplane’s operations; thus, it was not profitable. This marked the beginning of the aircraft’s slow decline.
The nail on the Supersonic Concorde’s operation was arguably the 2000 accident. On July 25, an aircraft destined for Paris suffered engine failure and crashed into a nearby hotel. All people on board, including a hundred passengers and nine crew members, died on the spot, as four pedestrians on the ground also lost their lives.
All Concorde flights were grounded after the incident for over a year. Though they later resumed operations, they did not recover from the tarnished public image arising from the accident. The underwhelming reception prompted airlines to ground the Supersonic Concorde permanently in 2003; they have not operated ever since.
Reasons for the Supersonic Concorde’s Failure
After 27 years of service, the Supersonic Concorde landed for the last time as it was retired by the last airline with the aircraft model in its fleet. Although it was a great commercial aircraft with cutting-edge technology that improved air travel, the Concorde had underlying issues that led to its downfall.
Here are some reasons why the aviation masterpiece doesn’t fly anymore.
1. Restricted Travel Routes
Despite the aircraft’s technological brilliance, the Supersonic Concorde was not allowed to fly on many routes. The main reason behind the restrictions was the aircraft’s sonic boom it produced as it flew. The supersonic jet noise was highly distractive as it could potentially shatter glass as it moved, making the aircraft quite disruptive to the communities living below.
As such, the Supersonic Concorde was banned from various airspaces as it was not allowed to take transcontinental flights. European countries such as West Germany, Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Switzerland, Canada, and the United States banned Supersonic Concorde flights. The restrictions greatly hindered airlines with the aircraft in their fleet from maximizing profits, slowly contributing to its downfall.
2. Ticket Prices
Building the Supersonic Concorde was quite expensive. Consequently, airlines tried to recover money through ticket sales. The aircraft was subsequently advertised as a luxury aircraft with highly high ticket prices. For instance, a return ticket from London to New York costs around $8,000 and could go as high as $11,000.
The tickets’ selling point was the reduced travel time, given the Supersonic Concorde’s speed. However, the pricing did not sit well with consumers as most people preferred cheaper luxurious options. The aircraft were rarely fully booked as only a few people could afford the tickets. Therefore, ticket sales did not make the anticipated profits, making the business financially unfeasible.
3. Customer Dissatisfaction
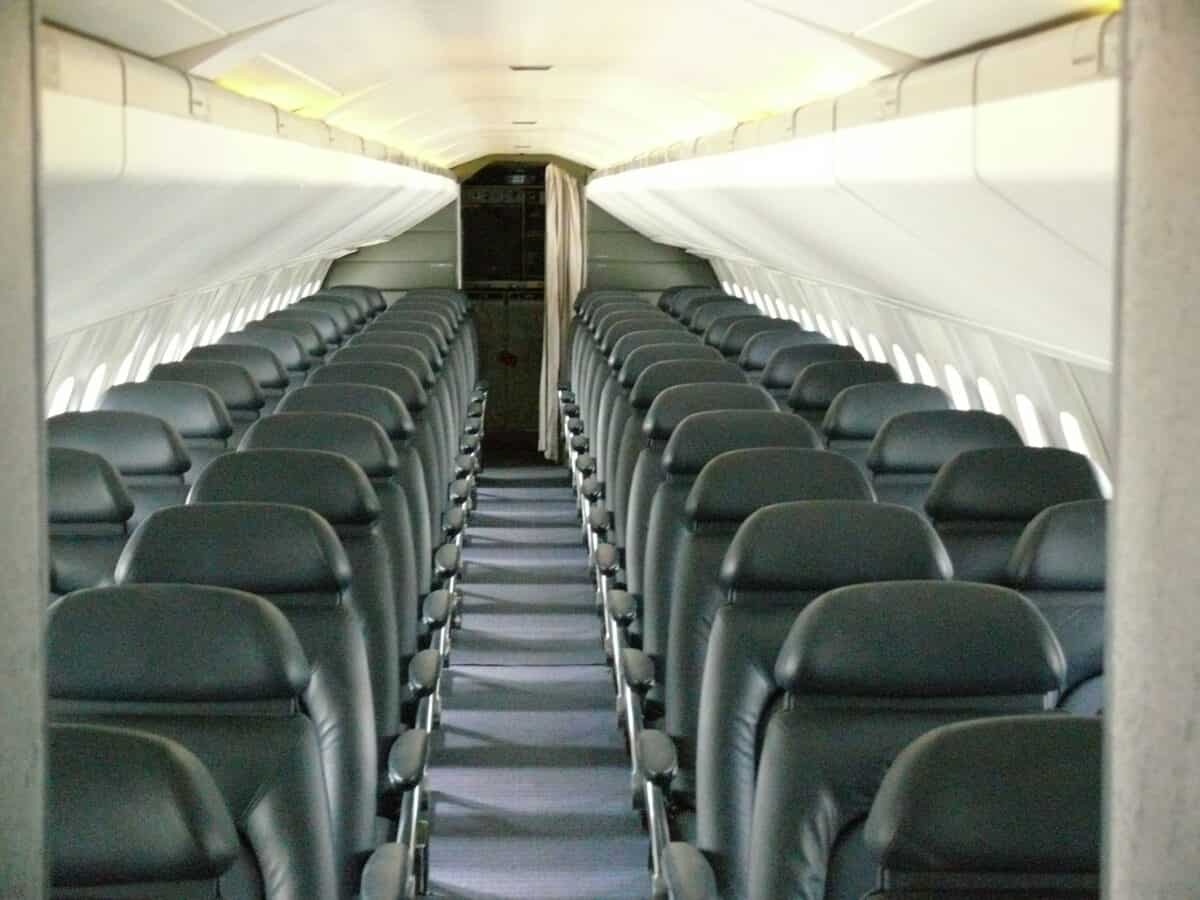
Another reason for the Supersonic Concorde’s failure was the underwhelming customer experience. Despite high ticket prices, the Supersonic Concorde flight experience did not give value for money. Foremost, the aircraft was too cramped for the prices it offered. When someone pays thousands of dollars for a plane ticket, they expect a luxurious setting with enough room to stretch and be generally comfortable on their flight.
On the contrary, the Supersonic Concorde did not have flatbed seats. The chairs only reclined 7 inches and were only 17 inches wide, restricting passengers’ comfort.
Similarly, the aircraft did not have in-flight entertainment. The only thing available to keep you busy during your flight were newspapers and magazines offered in the lounge since they could not fit on the plane.
Supersonic Concorde’s only advantage was reduced travel time compared to other airplanes. Nonetheless, customers were dissatisfied with the poor interior design and services that did not ensure their comfort. Consequently, most people did mind traveling extra hours, provided they got a great onboard experience at similar or cheaper prices.
The customer dissatisfaction experienced by Supersonic Concorde passengers culminated in bad publicity, which was a big blow to the aircraft. People avoided buying expensive tickets, leading to considerable losses.
4. High Fuel Consumption
Despite its great features, the Supersonic Concorde was not a monument of efficiency. Ideally, a great airplane has a low fuel consumption over long distances. Nonetheless, the Concorde was quite the opposite. Its engine needed corpus fuel amounts to keep it in the air. It was a fuel-speed converter.
Given the high fuel cost, the Concorde soon became unprofitable due to its high fuel consumption. All the money was directed toward fueling the plane, which did not make financial sense. Airlines slowly started grounding the aircraft, ultimately leading to the Supersonic Concorde’s failure.
5. High Maintenance Cost
Airplanes need regular maintenance to ensure they are in perfect flying condition. This includes regular inspections, servicing, repairs, and rectifying defects. The exercises are pretty expensive, even for a regular aircraft.
However, due to the Supersonic Concorde’s unique features, airplanes were forced to incur extra expenses in maintaining the aircraft. The aircraft’s jet engine required expertise to ensure it worked efficiently. Therefore, they had to pay experts and order expensive components. Accumulatively, everything needed to keep the Concorde in the air was too expensive to maintain, forcing its grounding.
6. Limited Range and Capacity
With a powerful jet engine powering it, you would assume that the Concorde could travel as many routes as possible to maximize the profits made. However, supersonic-speed aircraft had some limitations.
Although its primary goal was to reduce flight time, the Concorde could hardly fly from the UK to the Eastern U.S coast and didn’t have the range to make it to the Western coast. Similarly, the aircraft was only ideal for at least three-hour flights, so it could not travel short distances.
Even worse, Concorde has a small passenger capacity of 100, making it unprofitable given the high maintenance costs. Airlines, therefore, needed to sell tickets at high prices to fund their operations, given the limited capacity. Unfortunately, their prices did not resonate well with the target clients.
The airplanes’ limited range and capacity impeded profit generation and soon resorted to grounding the airplanes until they were no longer in use.

©By Ad Meskens – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=8459197 – Original / License
7. Unfavorable Release Date
It might be surprising to know that the aircraft’s release date significantly contributed to the Supersonic Concorde’s failure. The first commercial Supersonic Concorde took off in 1976, just three years after the first oil crisis. Although the crisis was over, several affected nations still had to ration fuel as the prices skyrocketed. Thus, airlines avoided operating aircraft that consumed considerably high fuel volumes but had little returns.
The Supersonic Concorde presented one of those high-maintenance aircraft that used up lots of fuel and made minimal returns. The aircraft burned around 26,000 liters of fuel every hour, carrying only 100 people. With the high fuel prices owing to the just concluded oil crisis, it was almost impossible to make profits with such limited passengers. Therefore, numerous airlines canceled their airplane orders and declined to add them to their fleet during the oil crisis.
8. Shuttered Consumer Confidence
The final hurdle leading to the downfall of the Supersonic Concorde was the unfortunate accident on July 25th, 2000. While the Air France 4590 was taking off, debris blew a tire and punctured one of its fuel tanks, causing a fire. The plane subsequently crashed into a nearby hotel and caused 113 casualties.
The accident significantly led to the decline of the Supersonic Concorde and halted its operations for over a year. Nothing was the same after the aircraft eventually returned to the sky. Consumers lost confidence in Supersonic Concorde over safety concerns, and ticket sales reduced considerably, leading to the grounding of all flights.
9. Competition from New Luxury Air Travel
After the launch of the Supersonic Concorde, airlines significantly improved their services and interior plane designs to offer luxurious travel and compete in the air travel industry. They offered comfortable seats, diverse meals, and excellent lounge services to improve their passengers’ flight experience. Additionally, passengers were offered these services at lower prices than the Supersonic Concorde.
By the late 90s, Supersonic Concord’s only advantage over the luxury air travel it was competing with was its superior speed. However, passengers widely preferred the comfort offered by the new luxury air travel over the opportunity to cut their time in the air by half. Concord struggled to compete with the emerging air travel options, gradually contributing to its failure.
Conclusion
Supersonic Concorde had the potential to become a unicorn in the aviation sector. However, it faced numerous operational and financial hurdles, leading to its inevitable downfall. Issues like limited passenger capacity, high maintenance costs, and unaffordable tickets undermined its competitiveness against other industry players, ultimately leading to the Supersonic Concorde’s failure.
Unfortunately, it’s unclear whether the Supersonic Concorde will ever fly again. It lost significant consumer confidence, meaning passengers may be unwilling to board it.
So why did the Supersonic Concorde fail? It all came down to its high-cost maintenance and bad timing.
Up Next…
- The Real Reason DeLorean Failed Spectacularly – Find out why one of the most promising sports cars failed.
- The Real Reason MySpace Failed Spectacularly – Learn why MySpace failed even after its seemingly successful launch.
- The Real Reason Solyndra Failed Spectacularly – Find out how Solyndra’s financial mistakes and culture led to its inevitable downfall.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Senohrabek/Shutterstock.com.