NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope will revolutionize our understanding of the universe, but who is James Webb? Discover the man behind the name and how his life led to this incredible astronomical instrument.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is one of the most exciting scientific instruments in recent years. It promises to push the boundaries of our understanding of the universe and unlock some of its greatest mysteries.
Even though the telescope is making news, many people aren’t aware of the individual who goes by that name. So, why was James Webb chosen to represent this telescope, and who was he exactly?
Who Was James E. Webb?
Webb was born in the small town of Tally Ho in North Carolina in 1906. Despite facing financial hardship, he excelled in school and eventually studied law.
After completing his degree, Webb worked as a lawyer for several years before beginning his career in public service. He held some government jobs, including one in the early 1930s as a member of the Senate Appropriations Committee.
His considerable background in public administration ultimately contributed to his selection as a NASA administrator.
A Career at NASA
In 1961, President John F. Kennedy appointed Webb as the second administrator of NASA. During his time working there, Webb oversaw significant advancements in space exploration.
As the administrator of NASA, James Webb played a crucial role in the Apollo program that eventually landed a man on the Moon. He oversaw the development and testing of the mission’s Saturn V Rocket. We have to remember that this was the height of the Cold War, and winning the space race was tremendously important for America at the time.
He was also responsible for the launch of several spacecraft, including the Pioneer and Surveyor missions. Also, he established the Lunar Orbiter program, which sent robotic spacecraft to map the Moon’s surface and identify possible landing sites.
Following a challenging time of division after the Vietnam War, Webb was instrumental in securing NASA funding. This is always the main problem with space exploration, but Webb managed to keep the agency well-founded during his tenure. He believed that the space program had the potential to inspire and unite the American people.
Despite his accomplishments, Webb also faced significant controversy. He came under fire for the Apollo 1 disaster in 1967, which claimed the lives of three astronauts during a routine test.
Webb passed on March 27, 1992, at 85 years old. Four years later, the development of JBWS started. The telescope’s name is a tribute to James Webb and how he paved the way for many essential discoveries in space history.
Creation and Development of the James Webb Space Telescope
The JWST’s first developments date back to the mid-1990s, when scientists and engineers began to explore a potential successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. They wanted a telescope that could observe the cosmos using infrared light.
At first, the telescope was named Next Generation Space Telescope. However, in 2002, the project was renamed in honor of NASA’s second administrator, James Webb.

©Dima Zel/Shutterstock.com
The development of the JWST has been a collaborative effort between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). NASA has been the primary driver of the project, while the ESA and CSA have provided critical instruments and support.
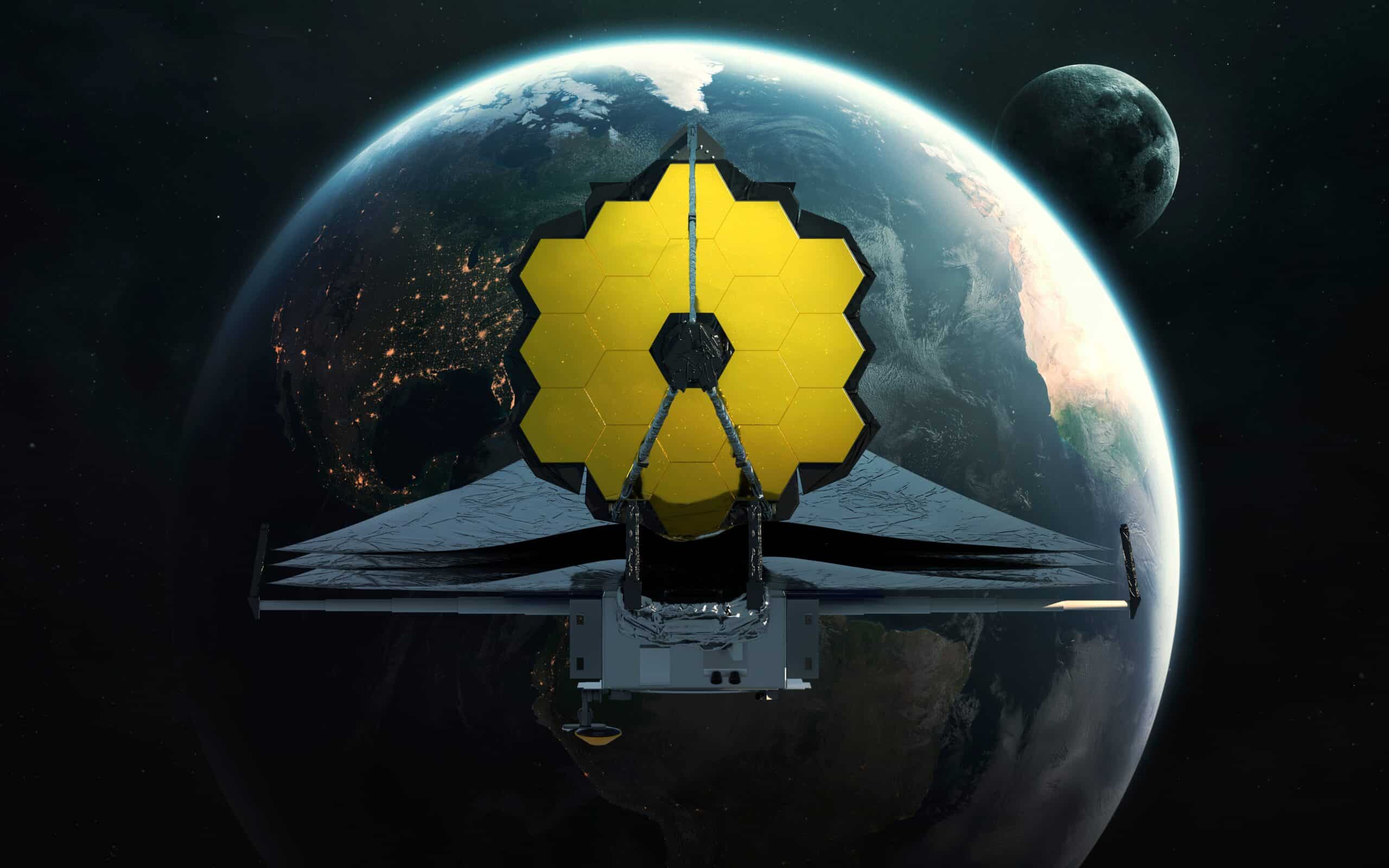
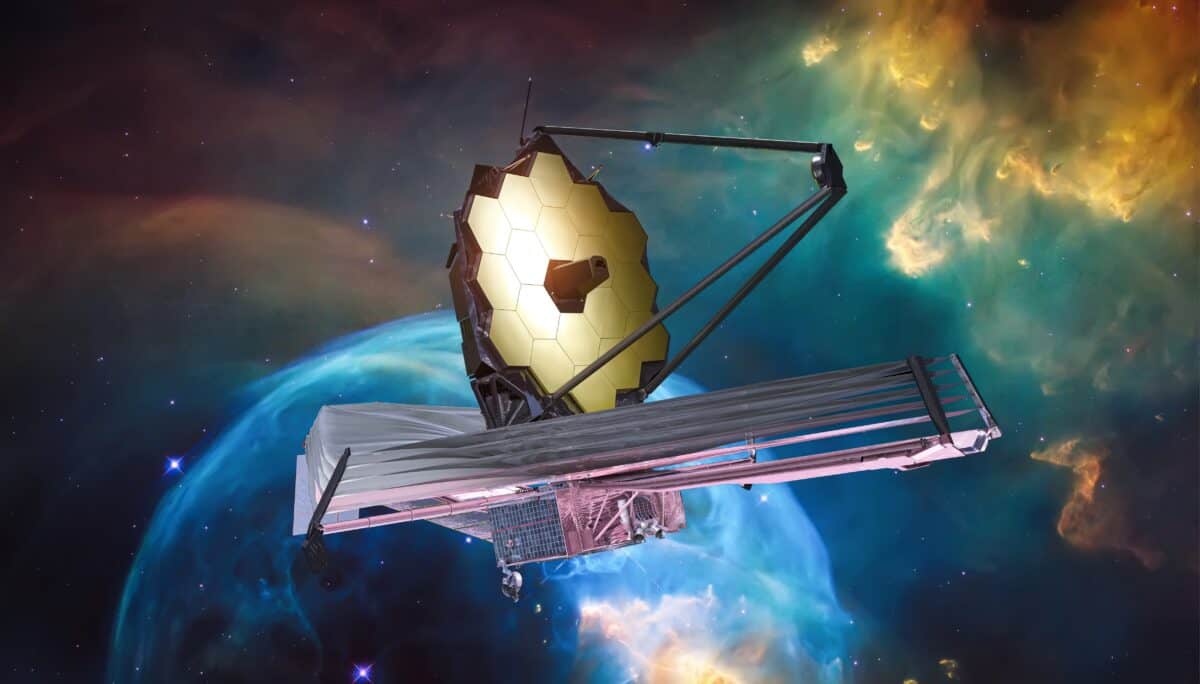
JWST’s construction was a highly complex process involving many individual components and subsystems. The telescope has a 6.5-meter primary mirror with 18 hexagonal segments and a tennis court-sized sun cover to shade it from the Sun.
The JWST is recognized as one of the most significant space exploration projects ever undertaken. It could significantly deepen our understanding of the universe and our place in it.
Just remember how immense it was when Hubble snapped all those astonishing photos, and think now that the JWST could deliver even better quality pictures of stars even further away.
How Does the James Webb Telescope Work?
The James Webb Space Telescope operates by collecting and analyzing light from some of the most distant objects in the universe. It uses a combination of advanced optics and infrared sensors to gather data about the light emitted by stars, galaxies, and other celestial bodies.
The telescope’s primary mirror consists of 18 hexagonal segments that can adjust independently to ensure that they are precisely aligned.
When the telescope points at a target, its primary mirror captures the light emitted by the object and reflects it onto a set of secondary mirrors. These mirrors then focus the light onto various instruments, including cameras and spectrometers, which analyze the light.
Another critical feature of the James Webb Space Telescope is its ability to observe in the infrared range. Infrared light can penetrate dust clouds and obstructions that would otherwise block our view of the universe, helping create detailed images.
Overall, the James Webb Space Telescope is an insanely complex and sophisticated instrument. It will enable scientists to explore some of the most profound mysteries of the universe.
Launch
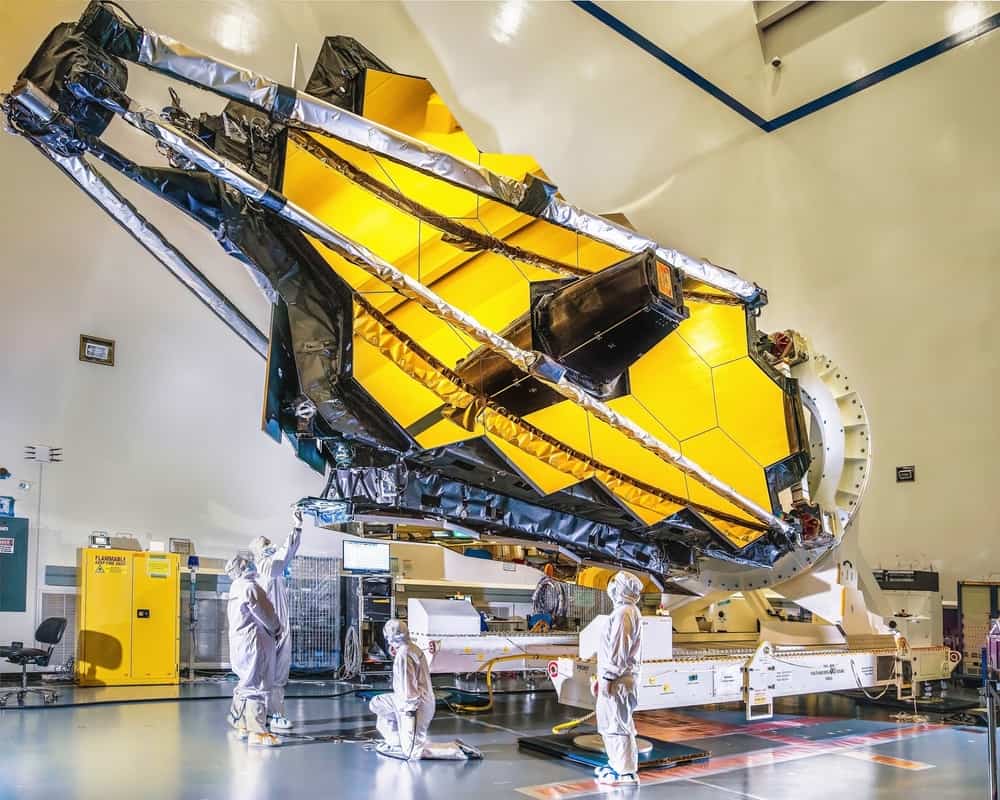
On December 25, 2021, the James Webb Space Telescope was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket, marking the beginning of a new era in space exploration.

.
©BEST-BACKGROUNDS/Shutterstock.com
Although its launch was at a slightly lower speed than necessary, the telescope was able to slow down during its journey away from Earth. As a result, it successfully reached orbit at L2 on January 24, 2022.
Scientific Results
With a few exceptions, experiment data will be kept confidential for one year for the exclusive use of the scientists leading the experiment. Afterward, the raw data will be made available to the public.
We have to remember that NASA still has close connections to the military, and certain discoveries or information could be wanted for those purposes. This means that there will always be a disconnect between what NASA receives and what the public gets.
Conclusion
Your main takeaway from this article should be that James Webb was a lauded administrator of NASA, who oversaw many crucial milestones in space exploration history. From the development of the rockets that landed us on the Moon to satellites and other technology, Webb deserves a place in history.
That’s why NASA decided to honor him in the mid-’90s by naming Hubble’s successor after him. The James Webb Space Telescope is equipped with modern technology that will allow us to pierce the secrets of the universe more than ever before. Therein lies its significance, and that’s exactly why it needs a name that befits such an achievement.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Vadim Sadovski/Shutterstock.com.