On February 6, 2018, Elon Musk became the first man to launch a car into space. Fitted with a mannequin in a spacesuit, “Starman” now rides an inner-solar-system orbit that extends past Mars. As incredible as that sounds, the event only brought attention to the spaceflight company’s new rocket, the Falcon Heavy.
But Elon isn’t stopping at cars; the main goal of SpaceX is to colonize Mars, and that’s going to take a much bigger vehicle. But bigger doesn’t quite do justice to the company’s newest design. Continue reading to learn more about Starship, the world’s largest rocket.
History of SpaceX
When considering modern spaceflight technology, one might immediately consider SpaceX, the rocketship company founded by Elon Musk. Initially created in 2002 with the express intent to colonize Mars, SpaceX — also known as Space Exploration Technologies Corp — has become one of the leading manufacturers of aerospace vehicles and parts. The company has made considerable advancements in rocket engines and reusable parts, helping bring down the cost of manufacturing and space missions.
With a background in software engineering, Elon Musk privately funded his first rocket design after selling his two companies, Net2 and Paypal. With nearly $100 million in investment, Musk signed his first mission contracts for the Falcon 1 with the Department of Defense (DOD). While the first missions were turbulent, eventual success led to the company’s funding for its next (and most successful) rocket, the Falcon 9.
SpaceX experienced incredible growth with its second rocket. In the last decade, the spaceflight company has attained numerous milestones, including:
- Becoming the first private company to launch, orbit, and recover a spacecraft.
- Being the first private company to send and dock a spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS).
- Being the first to land an orbital-class rocket’s first stage on an ocean platform.
- Becoming the first private company to send humans into orbit.
The engineers and technicians at SpaceX have continued to innovate. In 2019, the company launched 60 satellites that would become the first of an internet satellite constellation known as Starlink. The project intends to bring the internet to everyone worldwide. Starlink helps fund Musk’s largest endeavor yet; the Starship rocket.
What Is the Starship Rocket?
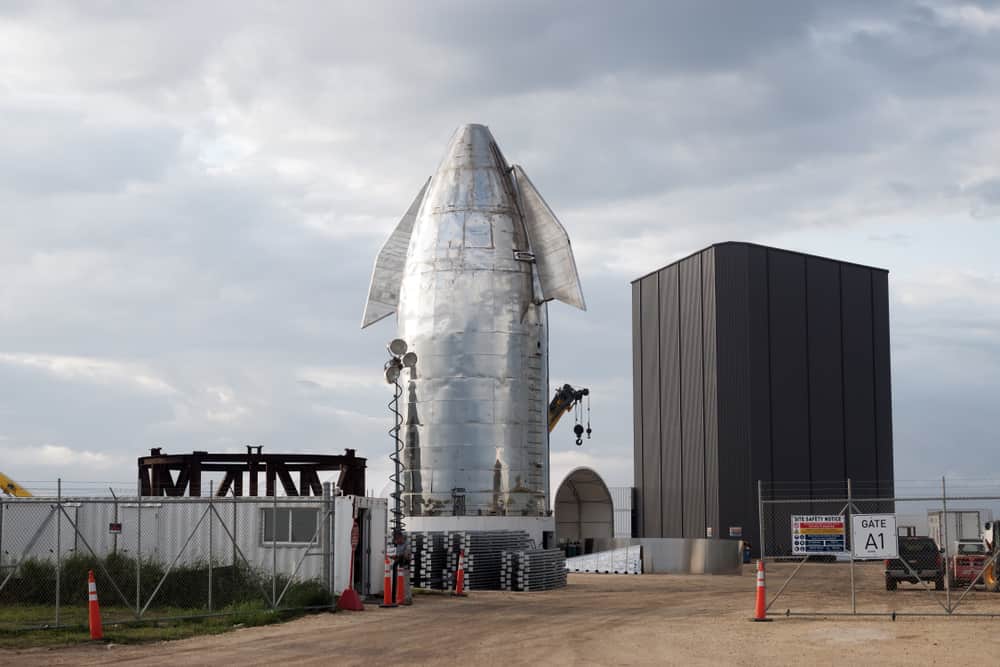

After 20 years of research and development, Elon Musk continues to pursue his urgent mission to colonize Mars. He intends to do this with his largest (emphasis on largest) project, Starship. The Starship is the biggest rocket in history at 400 feet tall and weighing 5,000 tons.
Also known as the BFR (Big Falcon Rocket), the Starship is designed to deliver payloads as heavy as 100 tons. This helps deliver the massive amount of materials needed to build spaceports on the moon and Mars. Starship will accomplish this feat with state-of-the-art spaceflight technology, including reusable parts, specially-designed engines, and one of the largest boosters ever created.
Reusable Spacecraft Parts
SpaceX has actively worked with reusable launch parts since 2012. The company has successfully managed to return and reuse orbital first stages and space capsules. Its Falcon 9 rocket relaunched 104 times, the second most only to the US Space Shuttle. However, no organization has designed a fully reusable system until Starship.
The rocket is considered two-stage-to orbit, with a first-stage rocket booster and a spacecraft. The two stages are made of stainless steel, which makes them strong enough to withstand g-forces and reentry. The reusable design of this large rocket system will drastically reduce the cost of missions over the vehicle’s life.
Raptor Engine
One of SpaceX’s products that make it the leader in spaceflight technology is its rocket engines. The company’s Merlin 1D, which propels the Falcon 9 first stage, produces a vacuum thrust of 690kN (kilonewtons, a measurement of force). The engine is capable of a thrust-to-weight ratio of 150:1, the highest produced by a rocket engine. To launch the Starship, which weighs almost 10x as much as the Falcon 9, SpaceX needs even more power.
Their answer to this problem is the Raptor, a methane/liquid oxygen (LOX) engine capable of 2.2MN. The new design can produce enough thrust with its full-flow staged combustion cycle. Unlike traditional open gas generator cycles, the engine uses much more propellant (all of its propellant) to get the turbine spinning. This makes it capable of drastically increasing the combustion chamber pressure.
The engine switches from kerosene (RP-1), the industry standard rocket fuel. While RP-1 is affordable and stable at atmospheric temperature, methane offers elite performance and burns clean, leaving no residue on rockets for better reusability. However, these engines are highly complex to design, and the only other models were created and tested in Russia in the 1960s.
Super Heavy Booster
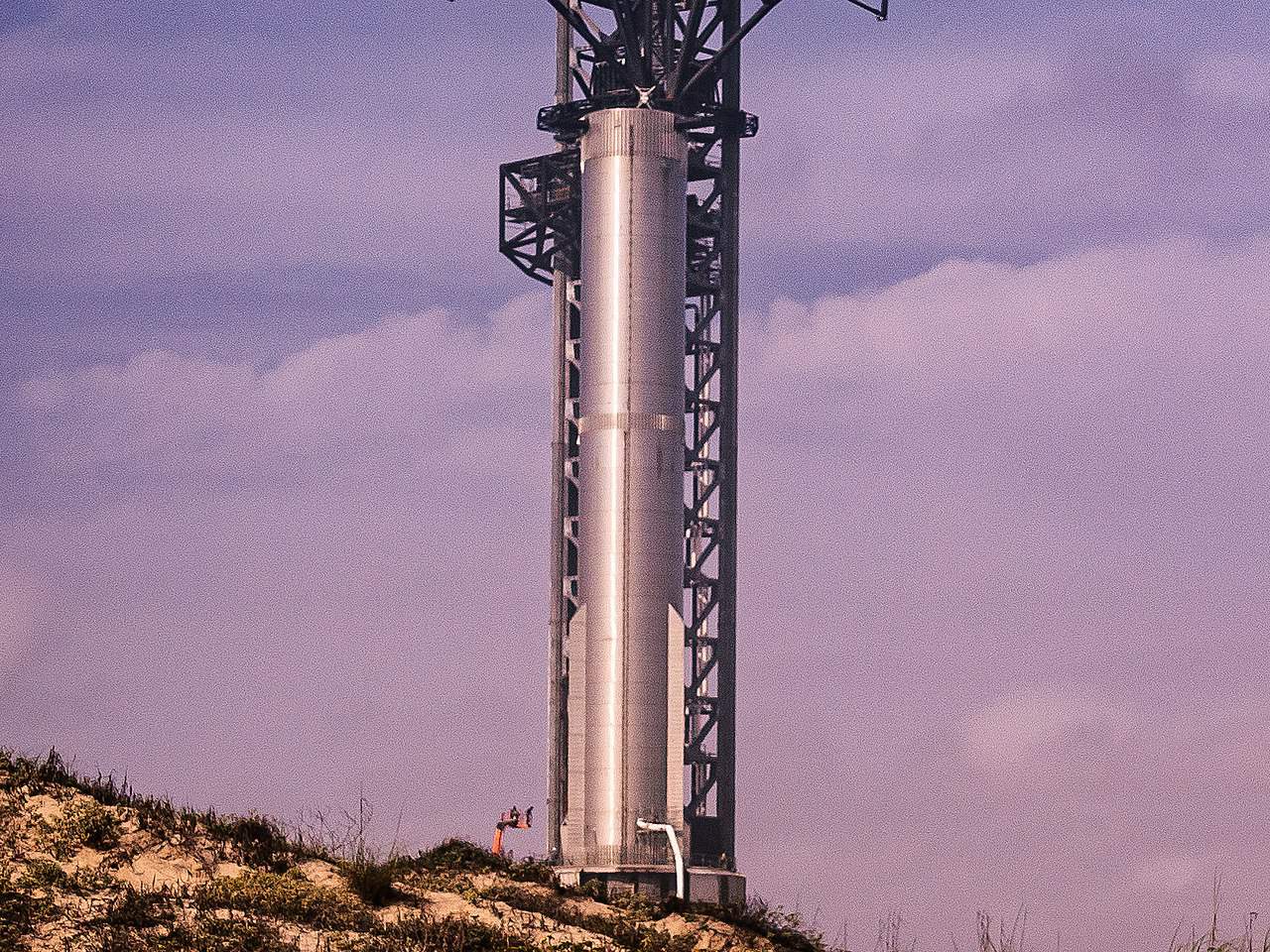

The Starship spacecraft is launched using SpaceX’s Super Heavy rocket booster. The first stage stands 230 feet tall and has space for up to 37 Raptor engines (making it twice as powerful as the Saturn V). As with its second stage, the Super Heavy is designed to return to Earth and land on its 6 legs.
Missions
Currently, Starship is planned to handle SpaceX’s larger commercial ventures. The spacecraft will deliver Starlink satellites into orbit and might make up a considerable portion of space tourism. An all-civilian expedition (called DearMoon) is scheduled to launch in 2023.
The spacecraft’s payload capacity also presents opportunities for space exploration. Starship can transport large space telescopes such as the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor. This allows scientists to scan for new planets similar to earth.
These are investment opportunities to fund the company’s underlying goal: colonizing Mars. The company will help establish lunar bases to secure jumping points to the Red Planet. Musk’s ambitious prediction for Starship’s first Mars landing is 2029.
Starship Specs
| Height | 120m/ 400ft |
| Total weight | 5,000t/ 10,000,000lb |
| Diameter | 9m/ 30ft |
| Payload (LEO) | 100+t/ 220,000lb |
| Stages | 2 |
| Engines | Raptor, Raptor Vacuum, Raptor Boost |
| Engine Count | up to 37 |
| Propellant Capacity | 1200t/ 2.6Mlb |
| Thrust | 500klbf/ 2.2MN |
| Reusability | Fully reusable |
| Cost | About 3 billion in development, about 150 million per launch |
| Launch Date | Unscheduled |
What’s Next For the Starship Rocket?
While the super-heavy spacecraft is the most advanced rocket in history, other companies compete in this generation’s Space Race. Spaceflight designers at Blue Origin have recently designed a methane/LOX engine that attempts to match the Raptor; Boeing is designing reusable crew capsules. Space exploration is quickly becoming humanity’s biggest endeavor, and Starship is guiding the way. The spacecraft is on course for an orbital test flight in the Fall of 2022.
SpaceX Starship Rocket Launch

The launch of SpaceX Starship was scheduled for launch on Monday, April 17th, 2023 but was delayed due to a problem with the pressurization system in the Super Heavy Booster.
SpaceX had planned to launch its Starship rocket from a private facility in Texas on Monday, April 17th, 2023, but with under 15 minutes left in the countdown, the company postponed the launch for at least 48 hours, announcing a “scrub.”
After years of regulatory work and technology testing, the Starship orbital launch represents a crucial moment. Despite multiple delays in development and FAA approval, SpaceX has always emphasized the experimental nature of the launch, initially planned for the summer of 2021.
Furthermore, Kate Tice from SpaceX stated that they are anticipating at least a 48-hour delay before their next launch attempt, which could happen on Wednesday, April 19th, 2023. She added that the timing for the next launch will be based on the data collected during the first attempt.
Finally, the launch was halted for the day by the flight director because of a problem with the pressurization system in the Super Heavy booster.
Looking for more on spaceflight? Check out these articles:
- SpaceX vs Virgin Galactic
- SpaceX’s Falcon 9 Rocket
- The 10 Largest Rockets of All Time
- The Largest Rocket Ever Created by Man
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Tada Images/Shutterstock.com.