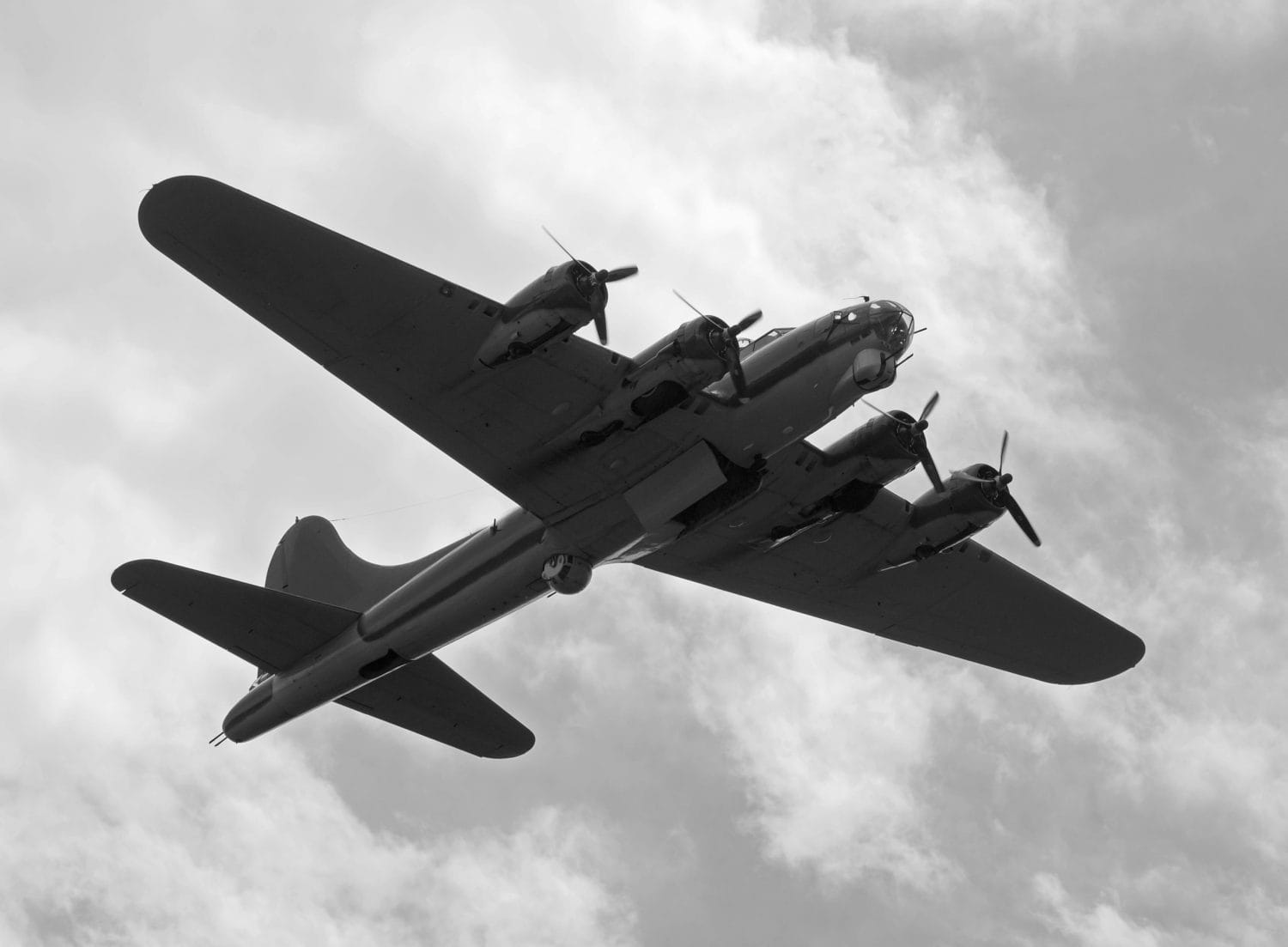
Best known as the “flying fortress”, the B-17 bomber was a four-engine plane used by the United States and its allies. Primarily used in Europe during World War 2, the B-17 is the third-most produced bomber of all time.
As a heavy bomber, the B-17 played a critical role in helping the Allies turn the tide against Germany and Japan. Of course, such an important aircraft needs to be in top working order, which is why 10 crew members were on every flight to help maintain readiness.
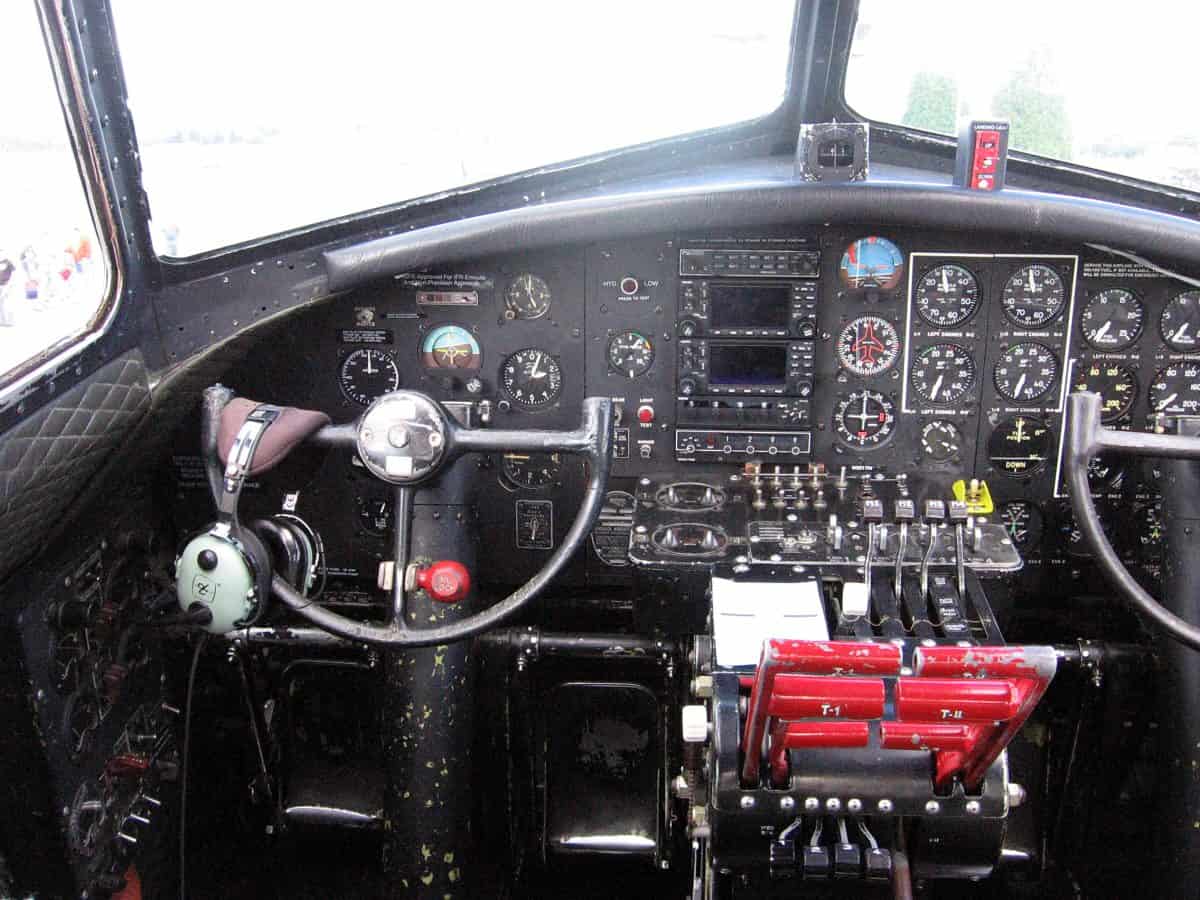
Pilot

©Mark Wagner / Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic license - Original / License
As the B-17’s commander, the pilot does far more than fly the plane. The pilot is fully in charge of the 10-man crew. It’s the pilot’s responsibility to keep up the crew’s camaraderie. How well a B-17 bomber would execute its mission was largely determined by how well the pilot could control the crew.
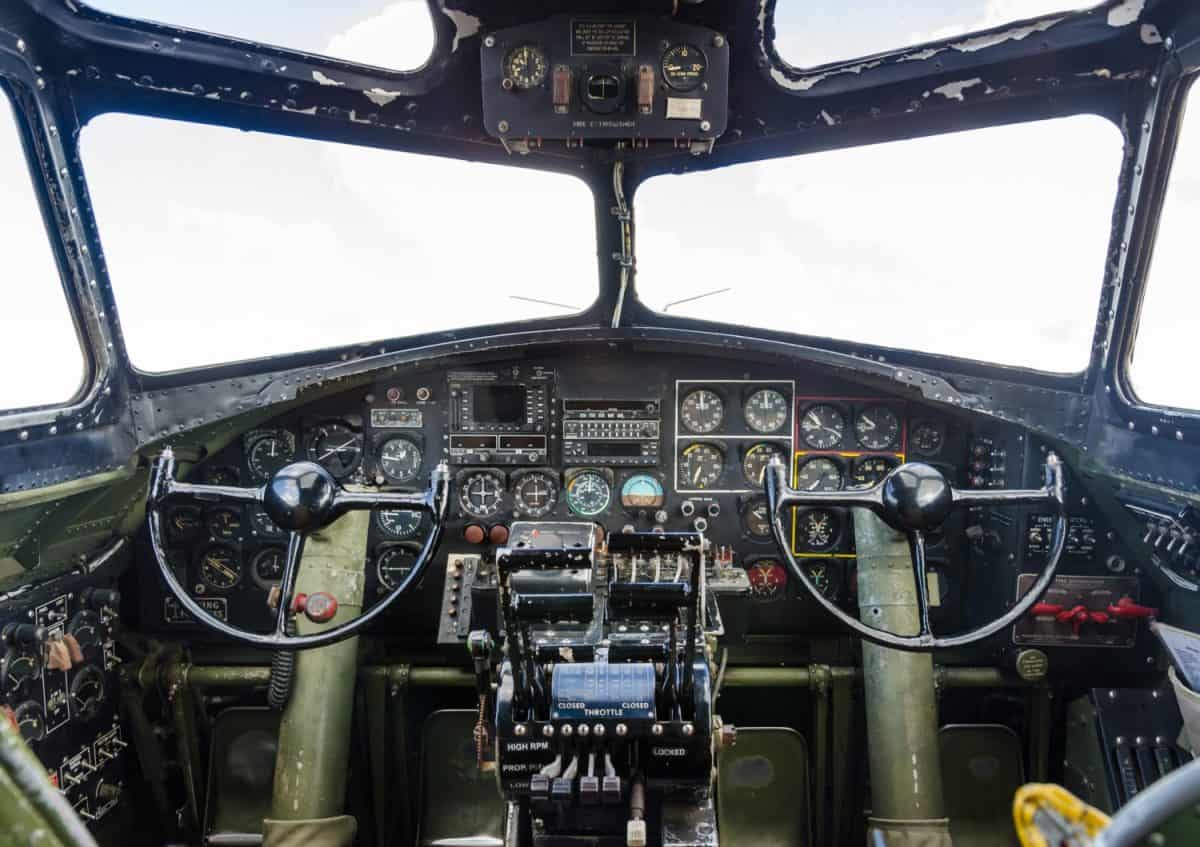
Airplane Commander

©Robert Sarnowski/Shutterstock.com
One of the most important responsibilities of every B-17 is to get to know the crew. The best pilots know all 9 crewmen like they know themselves. Every strength and weakness should be known to make a cohesive fighting unit while flying into battle.
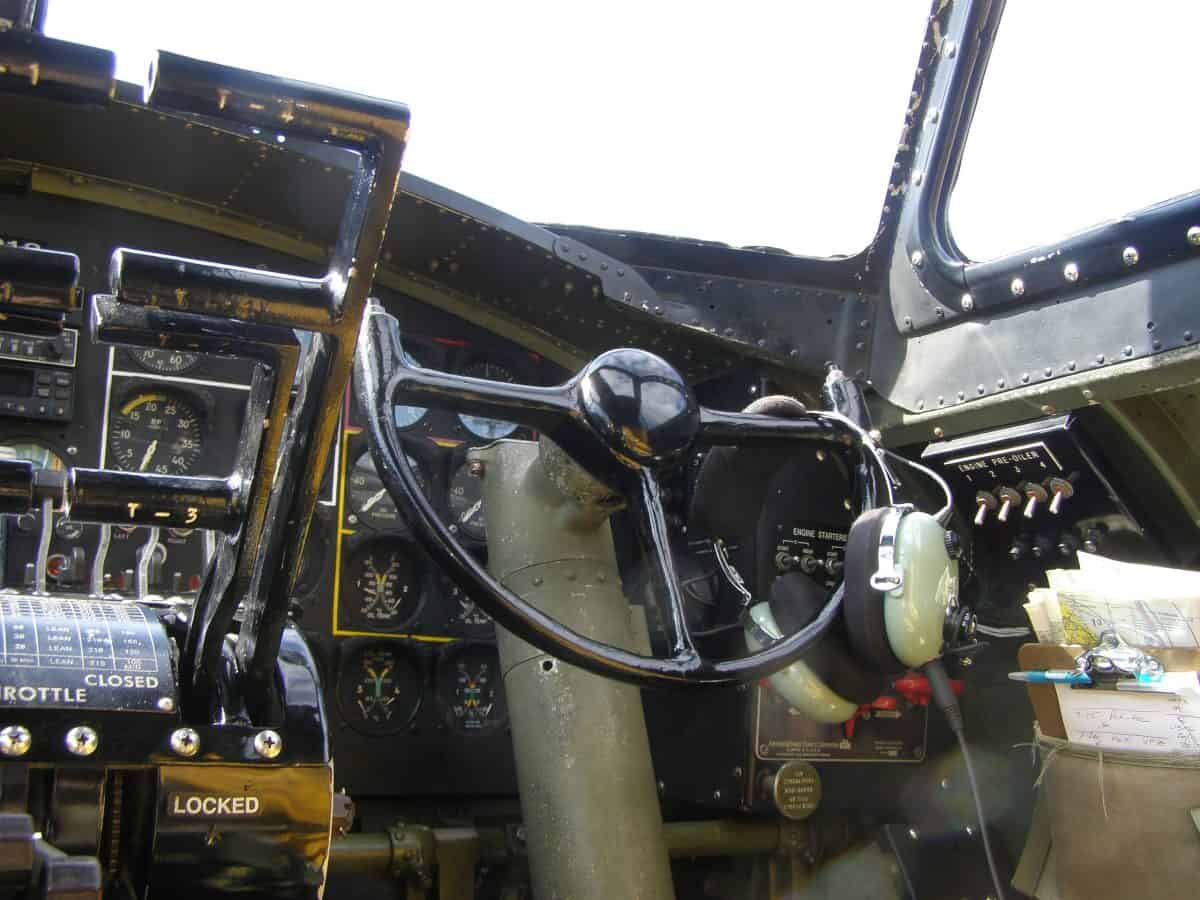
Copilot

©Chris Light / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license - Original / License
The second most important person on a B-17 bomber flight crew, the copilot should be able to fly the plane as well as the pilot. In the event a pilot is incapacitated, a copilot should be proficient in flying under any condition. Along with proficiency, a co-pilot must also make a log of the plane’s performance data.
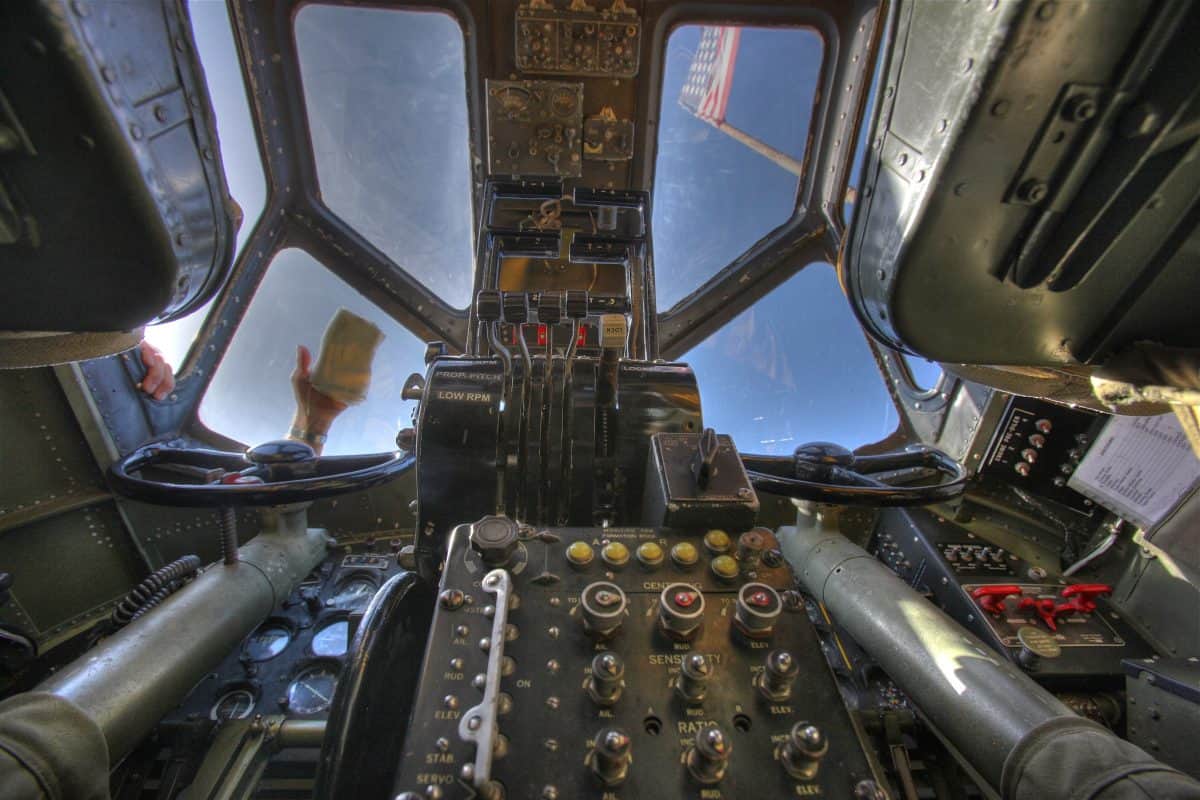
Second in Command

©Steve Jurvetson / Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license - Original / License
Any good pilot needs to remember the co-pilot is second in command. Plane and crew responsibilities should be shared between them both. Most importantly, it’s the job of any copilot to be ready to take command of the airplane and crew at a moment’s notice.
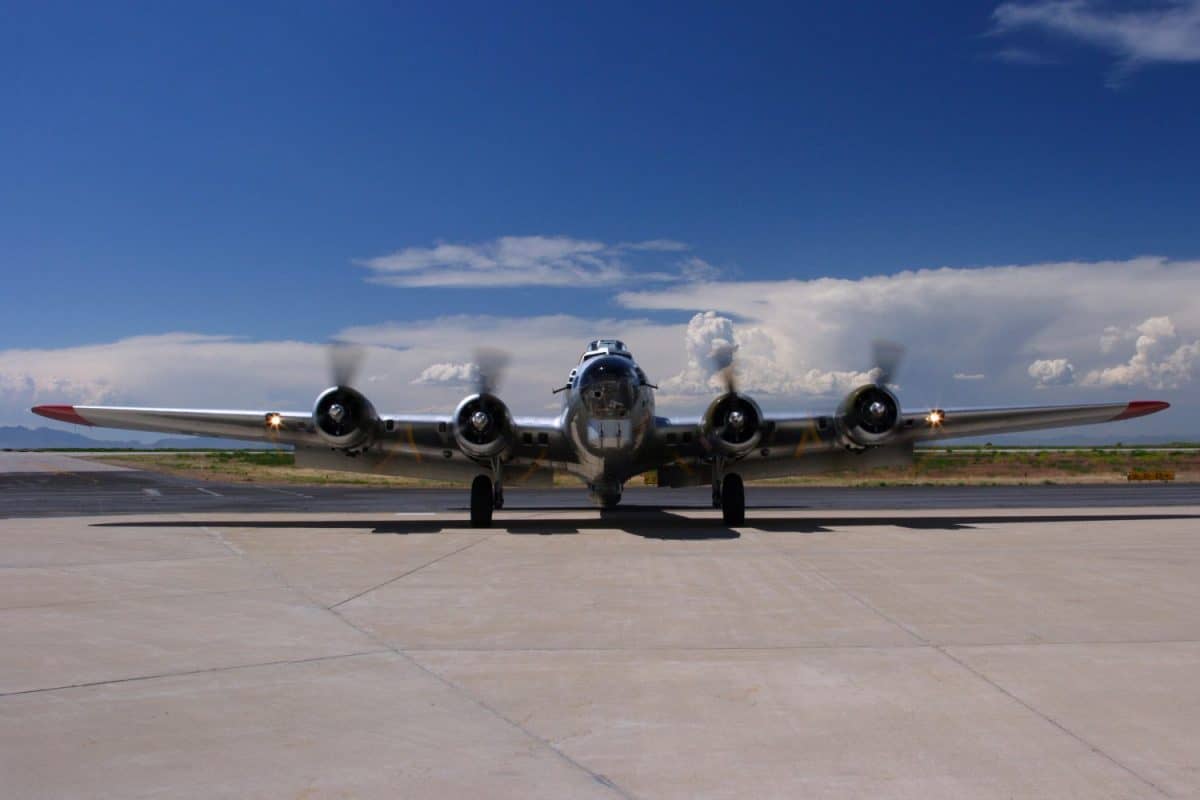
The Navigator

©Dave Lake/Shutterstock.com
One of the most important crew roles on the B-17 bomber is that of the navigator. This job is exactly what it sounds like. A navigator should know the position of the airplane at all times. No matter what methodology is employed, a navigator needs to know where the airplane is flying related to its target and base.
Navigation Methods

©Ivan Cholakov/Shutterstock.com
When on board the B-17 bomber, a navigator makes use of four different methods to track position. Pilotage, dead reckoning, radio, and celestial navigation are all critical skills a B-17 navigator must be familiar with.
Bombardier
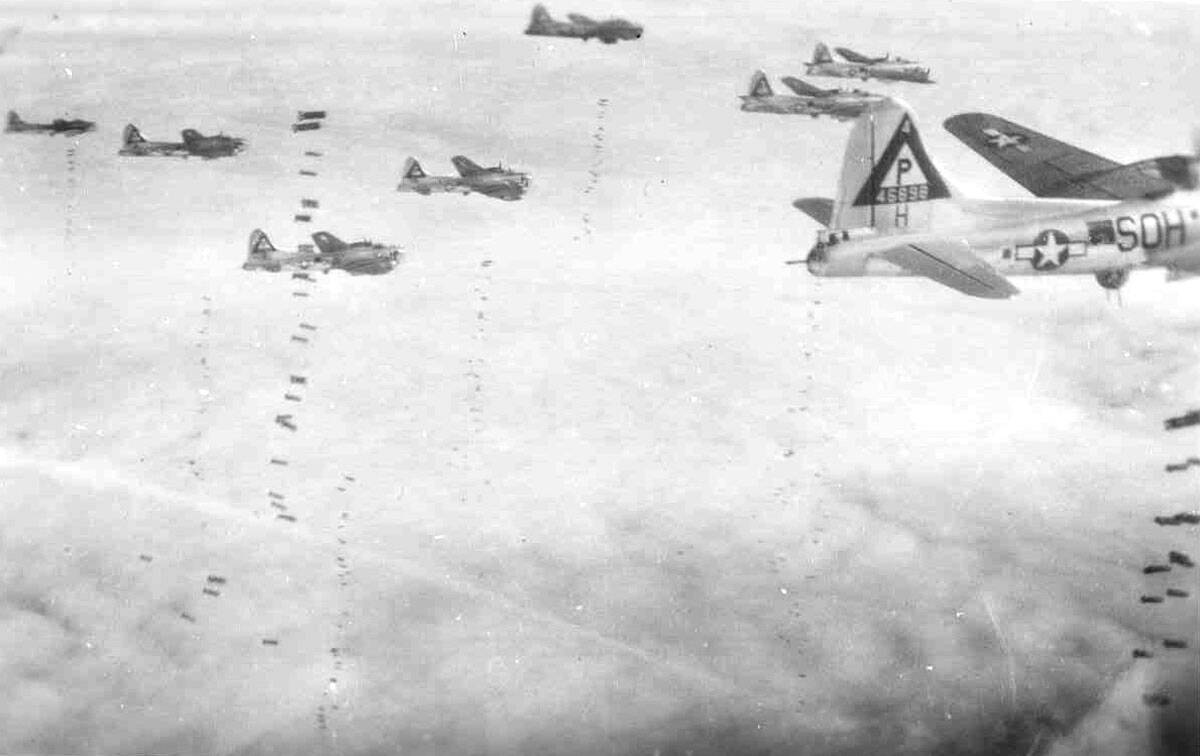

Just as this crewman’s title sounds, their responsibility is the reason why the B-17 bomber was designed. A bombardier is the one with a finger on the trigger to open the bomb bay doors and destroy the target.
Bombardier Trust
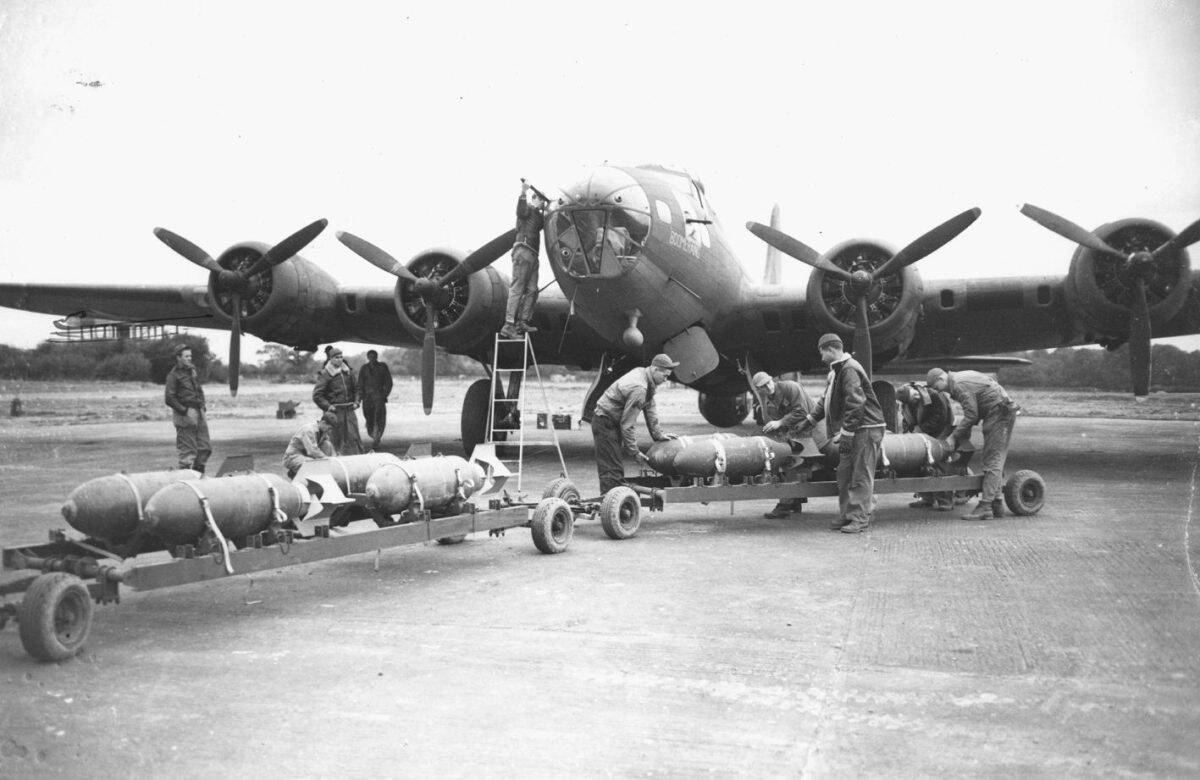

©United States Army Air Forces / Public Domain - Original / License
While a bombardier must know his bombsight like the back of his hand, they must also know how to rack all of the bombs. The bomb doors are also the responsibility of the bombardier to make sure they are fully operational.
Engineer

©Cavan-Images/Shutterstock.com
As the primary technical person on the crew, the job of a B-17 engineer was to know the physical plane better than anyone else. Engineers were typically provided advanced training on repairs to know the engine and all operational equipment. An engineer was also responsible for a B-17’s top gun turret when in battle.
Engineering Precision

©Airwolfhound / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license - Original / License
For a B-17 bomber to be truly effective, it had to be flying in the best possible shape. The engineer had to work closely with the whole crew while evading German or Japanese defenses and dropping ordinance. A great engineer can work other positions on a plane like the guns and radio.
Radio Operator

©Pi3.124 / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license - Original / License
Unsurprisingly, the role of a B-17 radio operator was to operate the radio. A radio operator assists the navigator with location to report positioning back to base. If there is any communication from the plane to the outside world, the radio operator handles it.
Radio Gunner

©Pi3.124 / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license - Original / License
Along with the radio role, the radio operator must be fully ready to use the .50 caliber machine gun. This gun placement was inside the radio room and was often used to defend against German fighter planes. The radio operator should know both this weapon and the radio.
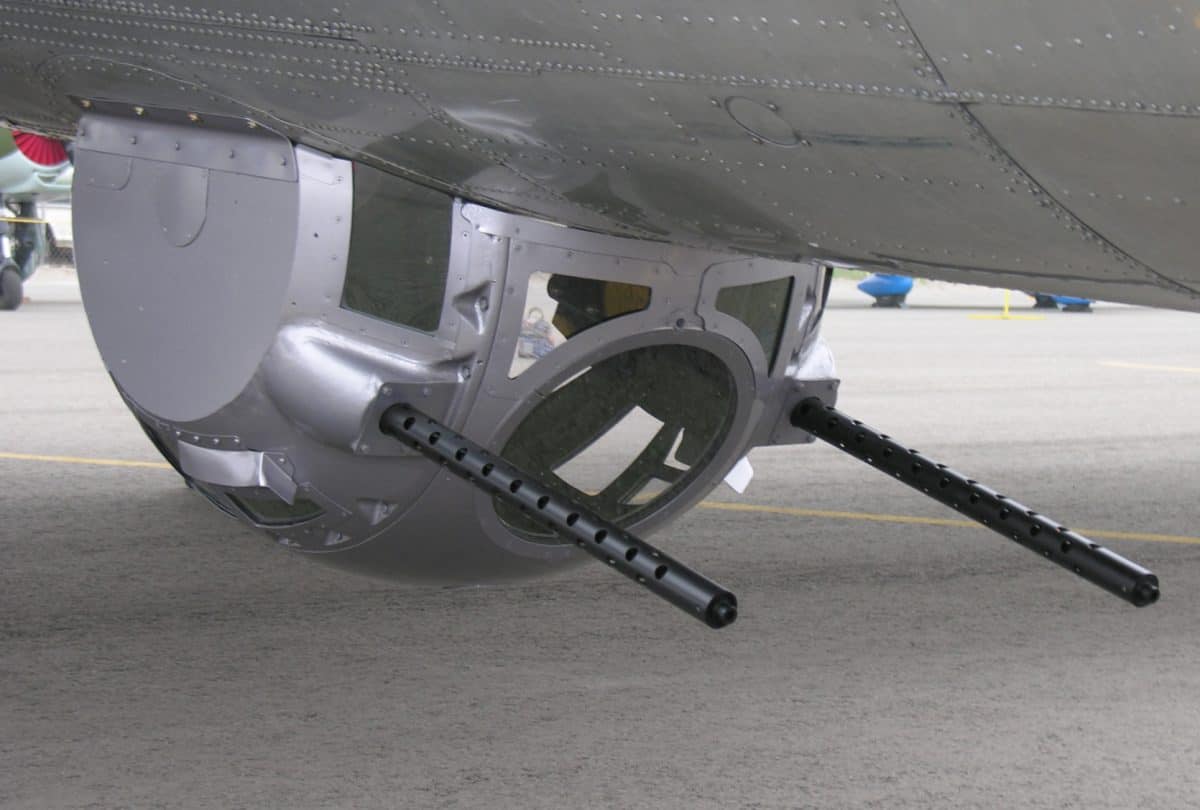
Ball Turret Gunner

©Greg Goebel / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license - Original / License
One of the most important defensive positions on a plane is the ball turret gunner. If this weapon is in use, it’s to defend the plane from enemy attacks coming from below the plane. Most ground attacks are out of the pilot’s view so a ball turret gunner can call out positioning.
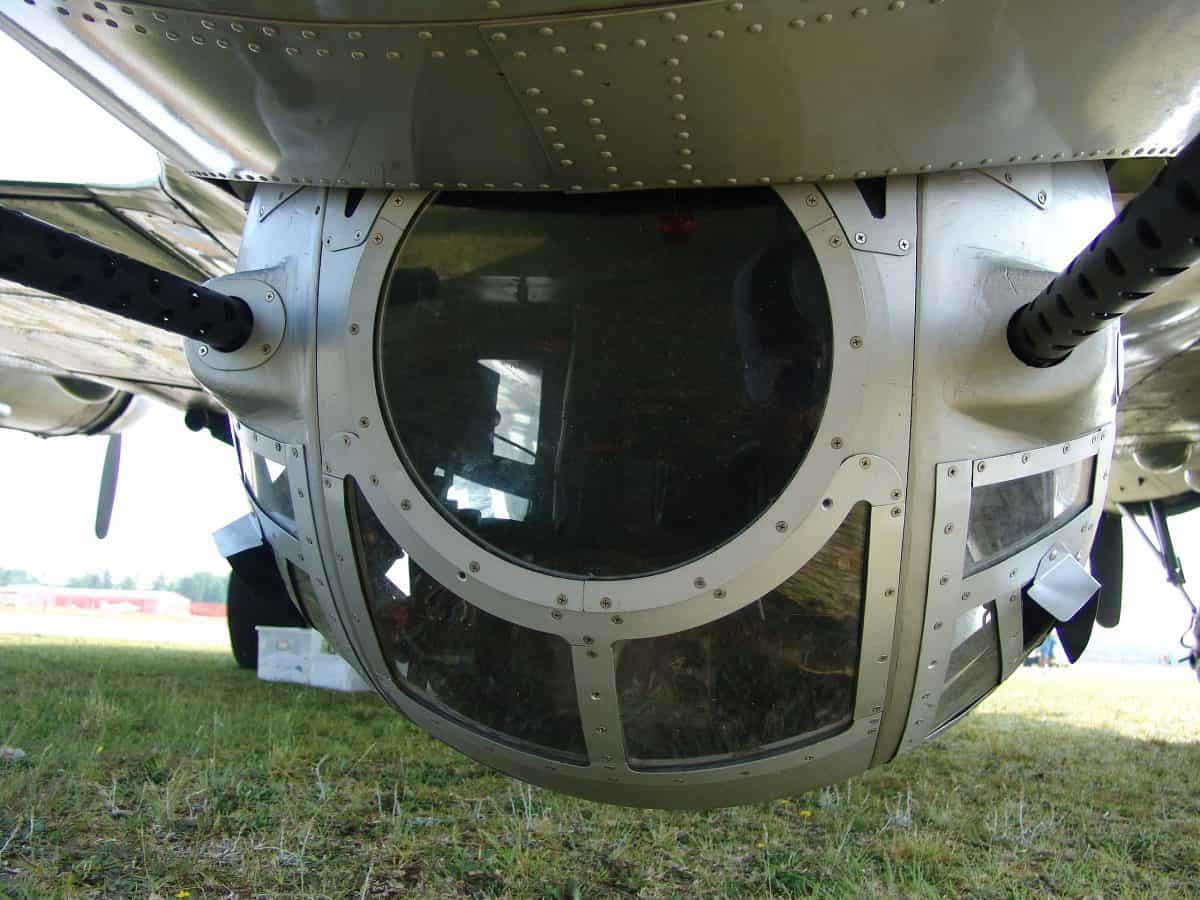
360 Defense

©Danleo~commonswiki / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license - Original / License
As the ball turret can turn a full 360 degrees, it gives the ball turret gunner a unique vantage point. It’s this ability that can make the difference in a bombardier knowing his targets or warning a pilot about a coming attack.
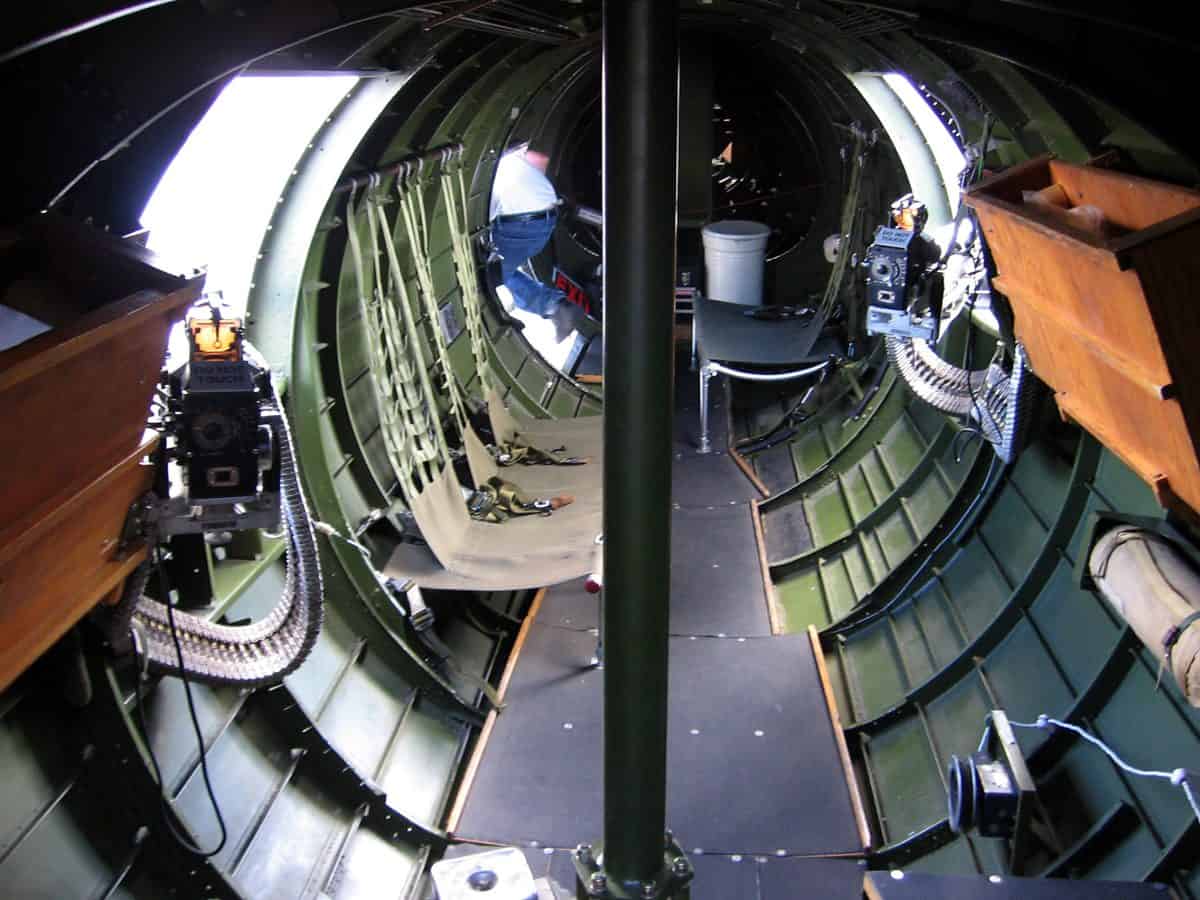
Left Waist Gunner

©Mark Wagner / Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic license - Original / License
Situated right in the middle of the B-17 bomber are the waist gunners. Set up on either side, the left waist gunner is responsible for protecting his side of the aircraft. This is his primary role and one he must be intimately familiar with.
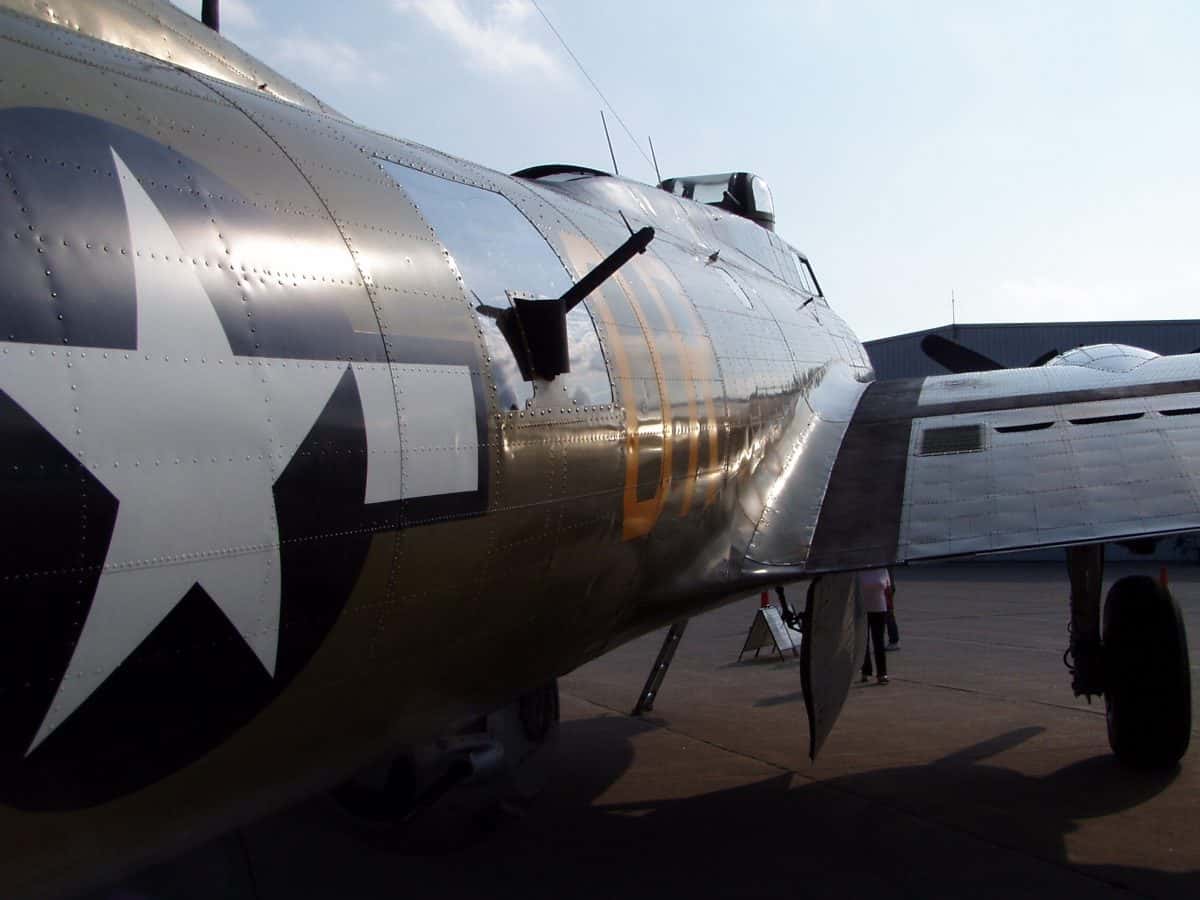
Left Responsibility

©Chris Light / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license - Original / License
As a gunner, the left-waist gunner should be completely familiar with the coverage area of his gun placement. He must also call out targets so other gunner positions are ready to continue an attack once out of the left-waist gun range.
Right Waist Gunner
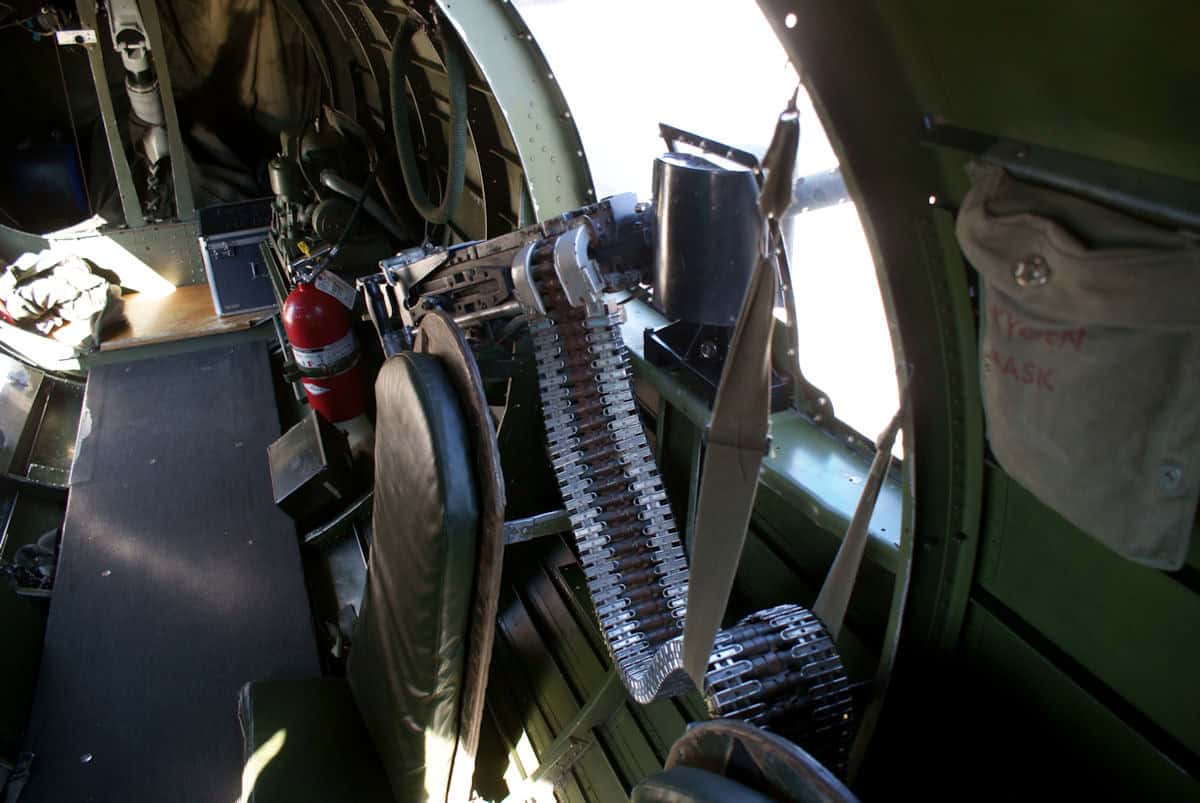

©Valder137 / Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license - Original / License
Similar to the left-waist gunner, this role must effectively cover the entire right side of the aircraft. A right-waist gunner should be able to strip down his weapon and rebuild it in case of any jams or issues.
Right Responsibility

©Chris Light / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license - Original / License
When the right-waist gunner brings his weapon to bear, he should be able to operate it with deadly accuracy. Gunners on B-17 bombers were skilled with their weapons because it could mean the difference between life and death.
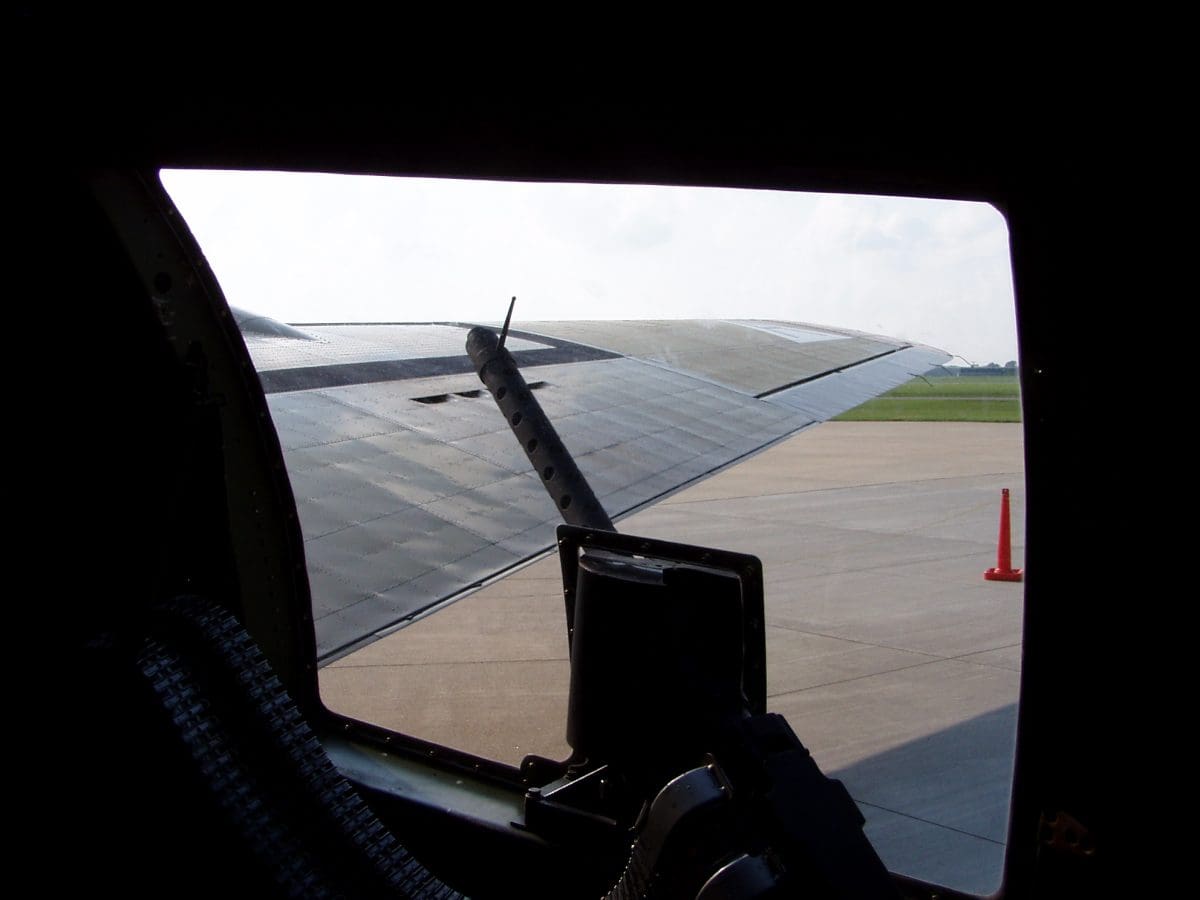
Tail Gunner

©Mark Wagner / Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic license - Original / License
While the position name speaks for itself, the tail gunner on a B-17 crew protected the crew in more ways than one. Of course, it was the main responsibility of the tail gunner to protect the rear of the aircraft. However, a tail gunner would also check everyone’s oxygen levels every 10 minutes.
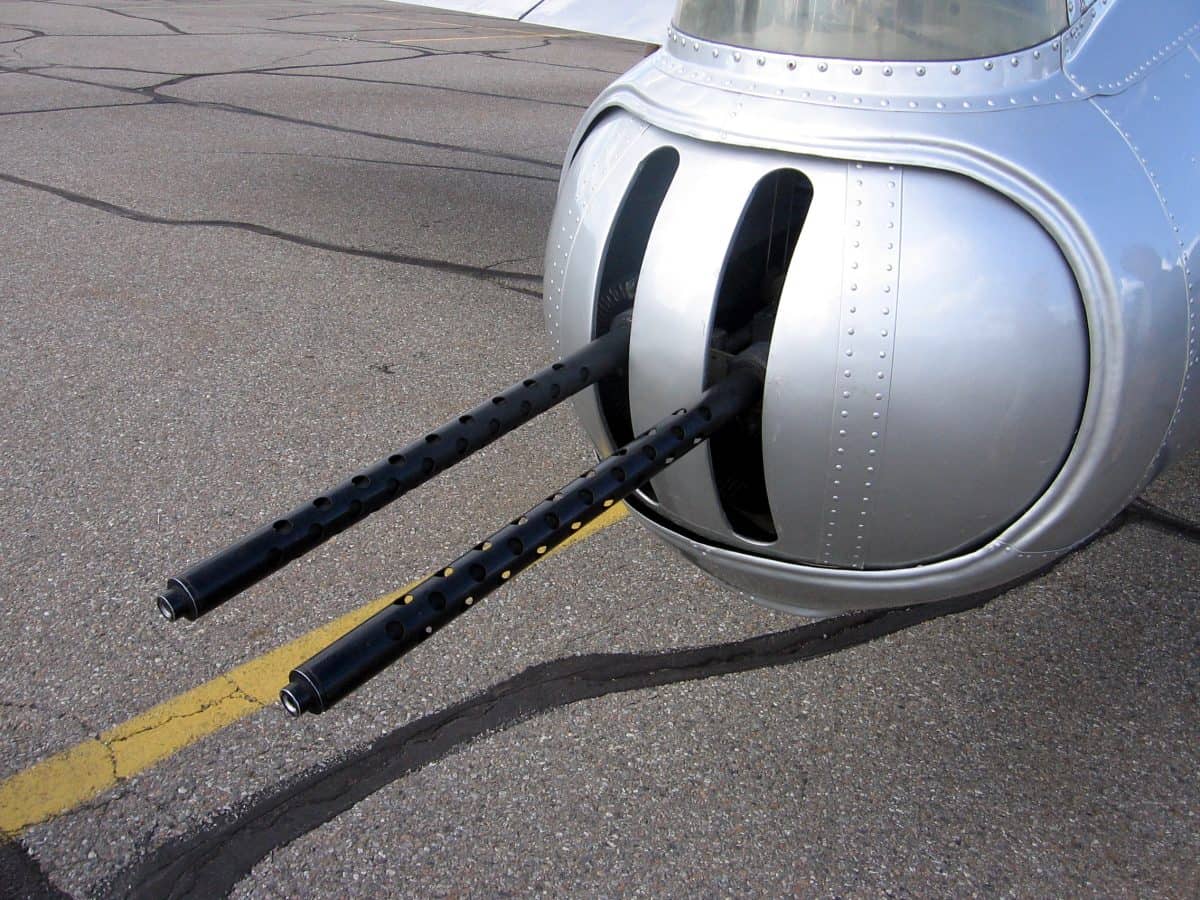
Tail Gunning

©Edward O'Connor / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license - Original / License
As the only person at the back of the plane, a tail gunner had visibility into the rest of the B-17 formation. If other planes were going down, the tail gunner would likely be in the best position to relay this info to the pilot.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Ivan Cholakov/Shutterstock.com.