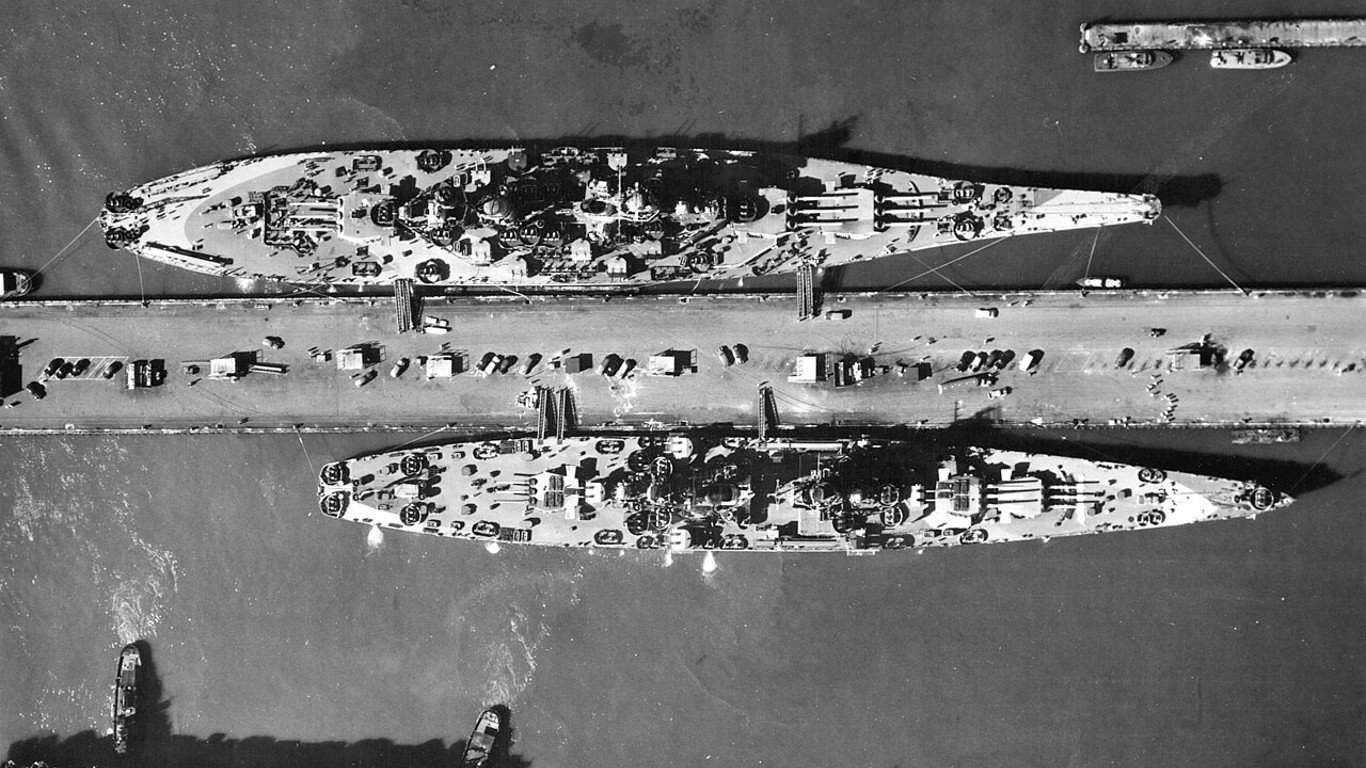
One major takeaway that the United States took away from World War II regarding military strategy was the importance of naval combat. When Japan failed to destroy the US aircraft carrier fleet, it left the US able to quickly rebuild its forces and eventually stop Japanese ambitions in the South Pacific alongside destroyers and cruisers.
29. Cleveland-class light cruiser
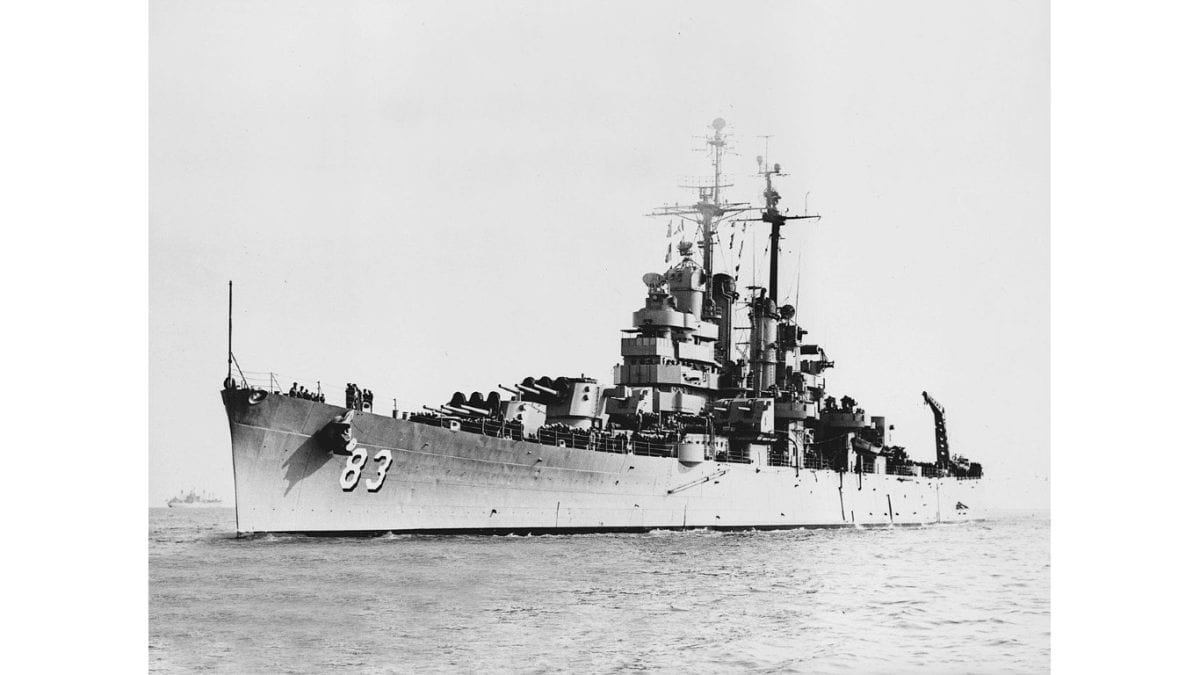

- Main armament: 4 x 152 mm/.47-cal triple Mark 16 guns, 6 x 127 mm/.38-cal twin guns, 4 x 40 mm quad Bofors guns, 6 x 40 mm twin Bofors guns, 10 x 20 mm twin Oerlikon cannons
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 29
- First year launched: 1941
- Crew: 1,255
One of the most manufactured ships during the Second World War, the Cleveland-class light cruiser heavily emphasized providing cover for the larger ships in its fleet. While it didn’t have the same armament or weaponry as a destroyer, the purpose of a cruiser was no less critical as it looked to provide both support against aerial and surface attacks.
28. Brooklyn-class light cruiser
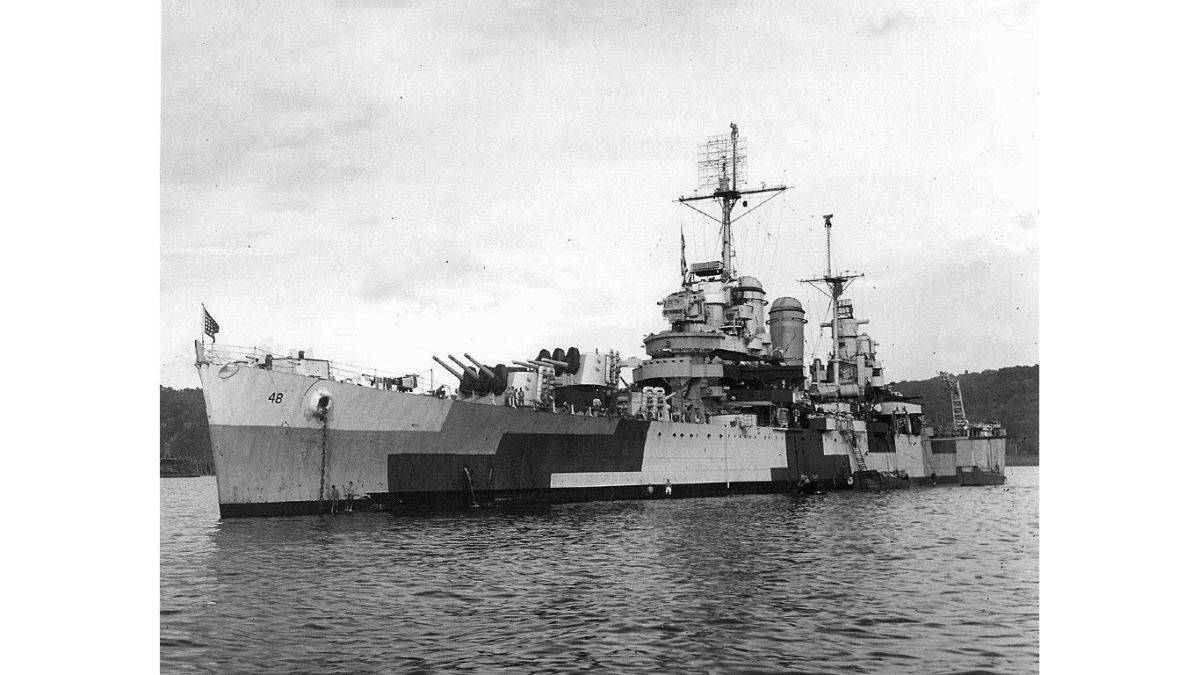
- Main armament: 5 x 152 mm/.47-cal triple guns, 8 x 127 mm/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 8 x .50-cal machine guns
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 9
- First year launched: 1937
- Crew: 868
Like many other light cruiser ships during the Second World War, the goal of the Brooklyn-class light cruiser was to provide support for larger boats in its convoy. As a result, these ships were well-armed, with a heavy emphasis on fending off aerial attacks.
27. Omaha-class light cruiser
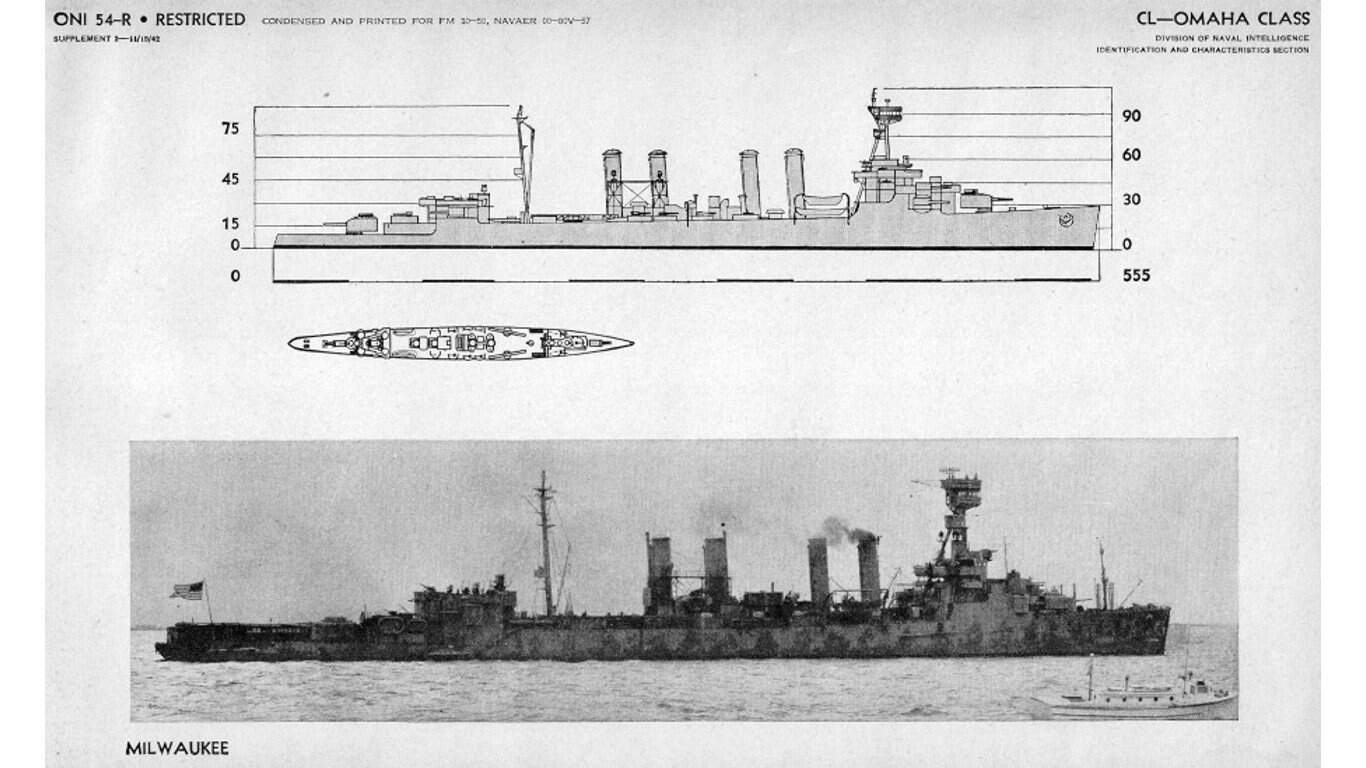
- Main armament: 12 x 6 in/.53-cal guns, 2 x 3 in single anti-aircraft guns, 10 x 21 in torpedo tubes
- Number built: 10
- Launched: 1921
- Crew: 458
Omaha-class light cruisers were designed and built after WWI, and their weapons systems reflected this. This class of ships was initially intended as a high-speed ocean scout and would inspire later classes of light cruisers, including the Brooklyn class. As such, the armament for these vessels consists of lower-caliber guns intended for anti-aircraft measures.
26. St. Louis-class light cruiser

- Main armament: 5 x 6 in/.50-cal triple Mark 6 guns, 8 x 5 in/.50-cal Mark 8 guns, 16 x 1.1 in guns, 12 x 20 mm saluting guns, 1 depth charge rack
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1938
- Crew: 888
Only two St. Louis-class light cruisers, commissioned by the United States Navy in the late 1930s, were built – the USS St. Louis (CL-49) and USS Helena (CL-50). This class of ship was meant to improve on the Brooklyn-class with better combat survivability and anti-aircraft guns.
Originally designed to serve as convoy escorts, these warships featured Mark 6 guns, known for their accuracy and destructive capabilities. They were grouped into five triple turrets along their decks. This and a series of lower-caliber anti-aircraft guns helped the class play a key support role.
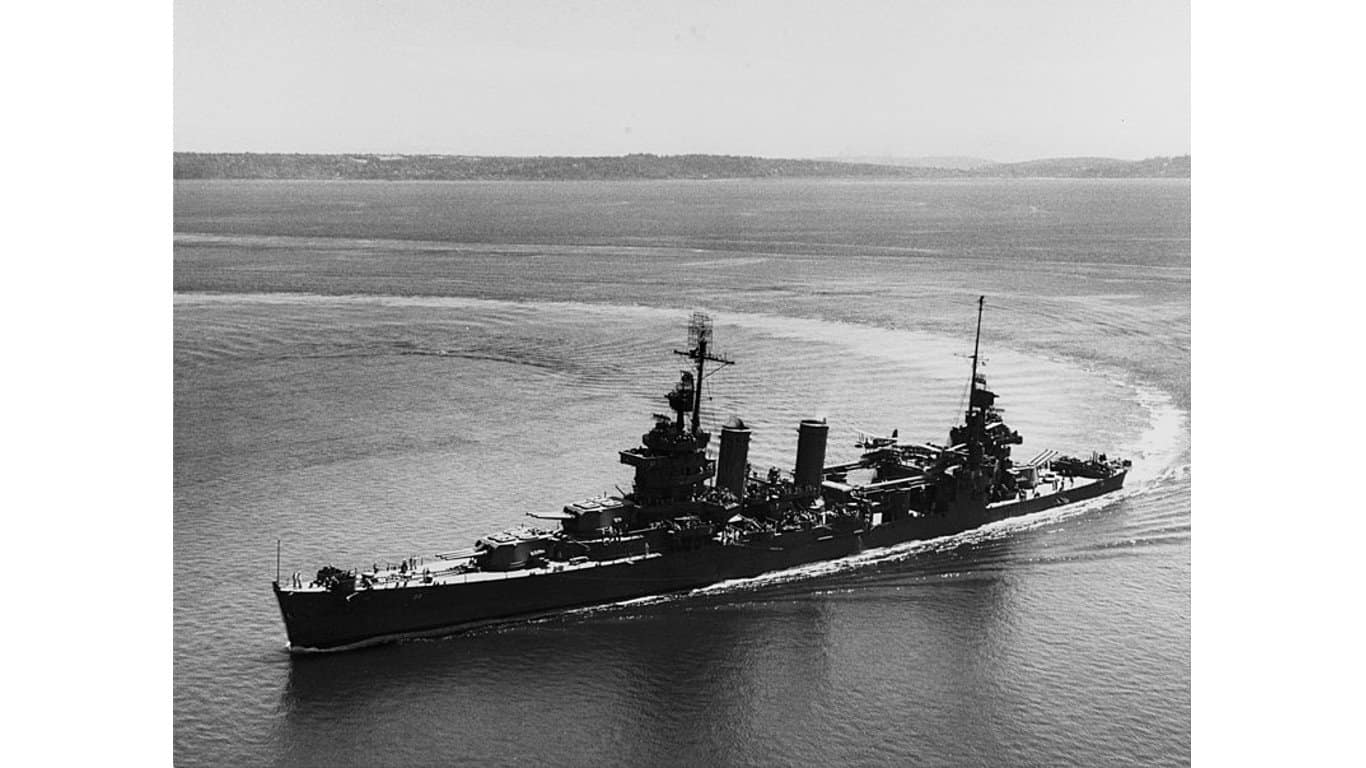
25. New Orleans-class heavy cruiser

- Main armament: 3 x 200 mm/.55-cal triple guns, 8 x 130 mm/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 2 x 37 mm saluting guns
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 7
- Launched: 1933
- Crew: 899
The New Orleans class of heavy cruiser warships was initially constructed during the 1930s, before the war. Their primary armament consisted of nine .55 caliber guns mounted in three triple turrets, delivering long-range firepower against enemy vessels. Additionally, the cruisers were equipped with various secondary armaments, which provided support against aerial assaults.
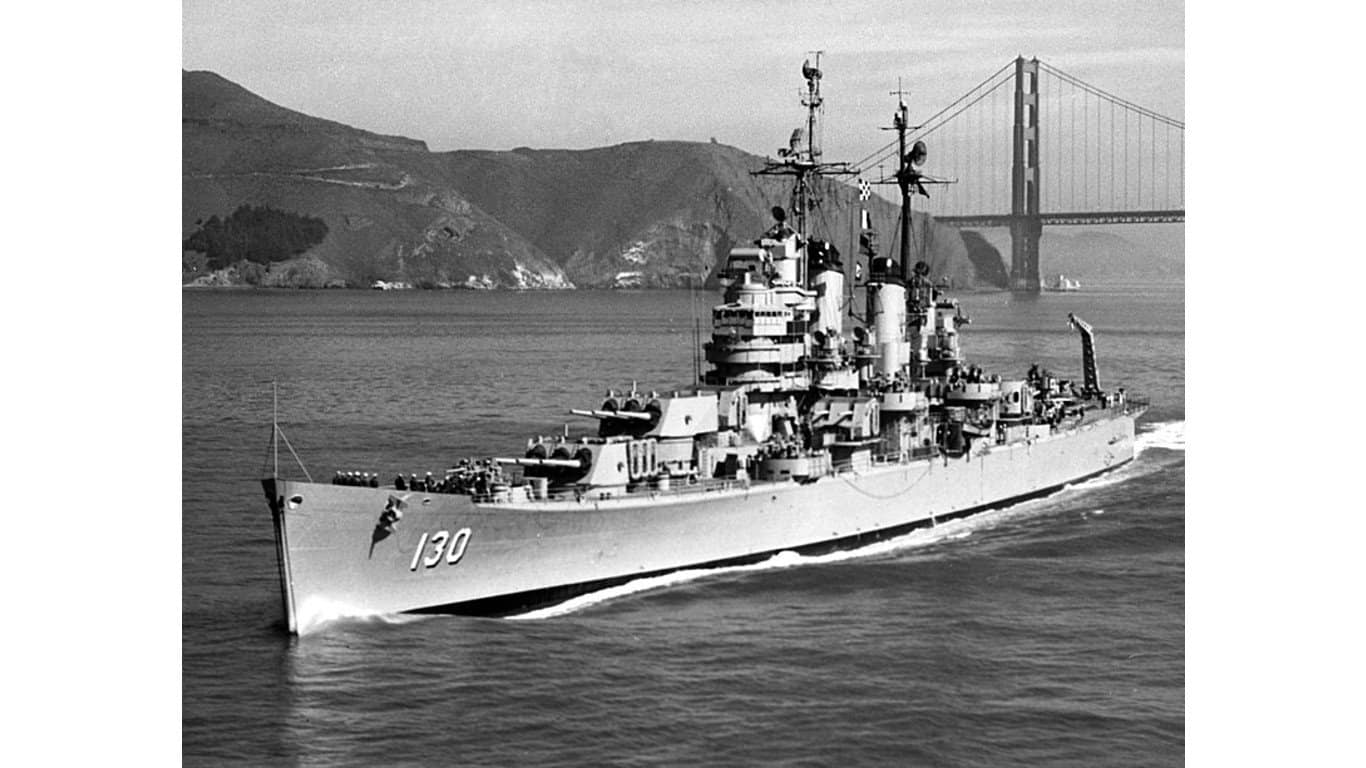
24. Baltimore-class heavy cruiser

- Main armament: 3 x 203 mm/.55-cal triple guns, 6 x 127 mm/.38-cal twin guns, 12 x 40 mm quad Bofors anti-aircraft guns, 24 x 20 mm Oerlikon anti-aircraft cannons
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 14
- Launched: 1942
- Crew: 1,700
The USS Saint Paul (CA-73) entered WWII late in the conflict, but it was one of the more technologically advanced ships, as reflected in its armament. The USS Saint Paul had nine 203 mm-caliber cannons and 12 more 127 mm-caliber cannons flanked by Oerlikon anti-aircraft cannons. Historically, this ship is significant because it was in Tokyo Bay to participate in the formal surrender ceremony.
23. Pensacola-class heavy cruiser

- Main armament: 10 x 203 mm/.55-cal guns, 4 x 127 mm/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1929
- Crew: 653
The Pensacola class’s primary firepower consisted of 10 203 mm guns mounted in four turrets, which provided substantial range and striking power during engagements. The secondary armament featured 127 mm dual-purpose guns complemented by an array of anti-aircraft weaponry. The lead ship of this class, the USS Pensacola, played a key role in aerial defense and rescue during the Battle of Midway.
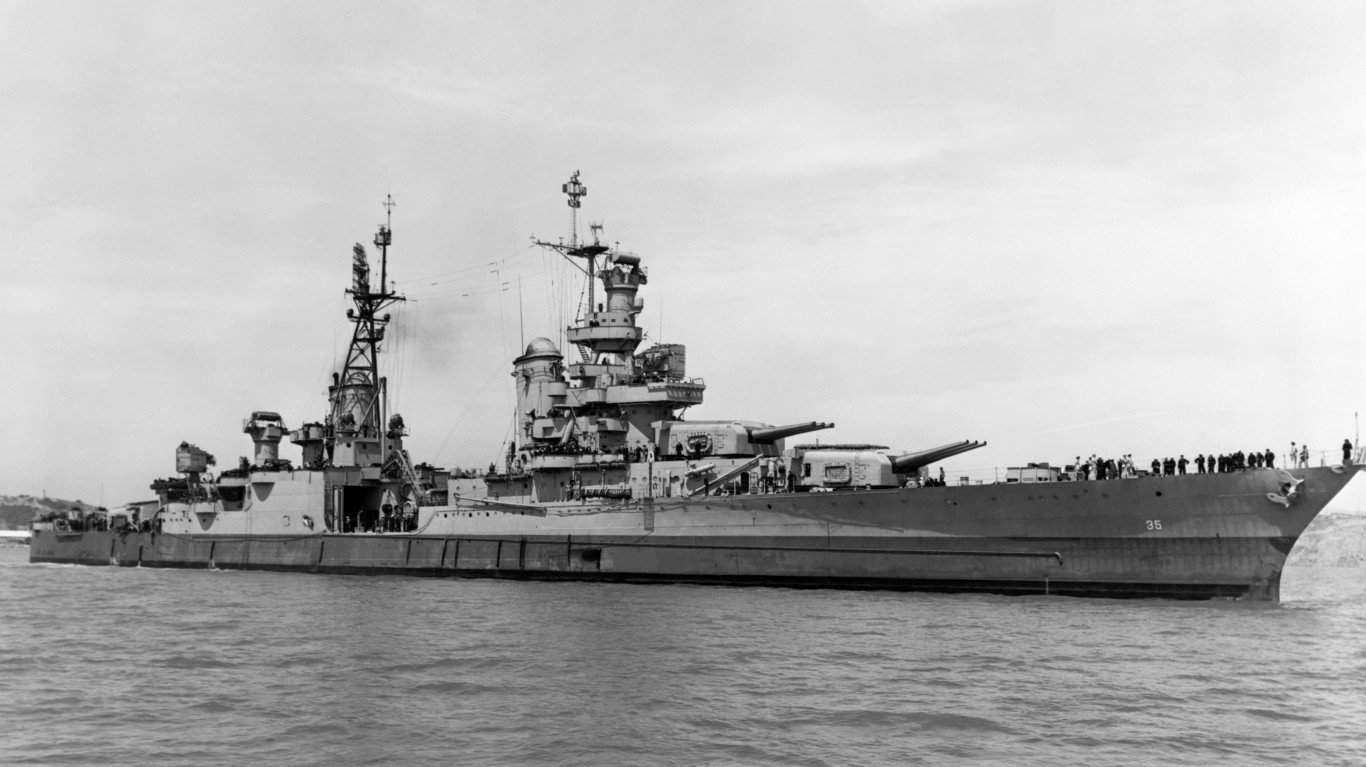
22. Portland-class heavy cruiser

- Main armament: 3 x 8 in /.55-cal triple guns, 8 x 5 in/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 2 x 47 mm 3-pounder guns, 4 x 40 mm quad Bofors anti-aircraft guns, 4 x 40 mm twin Bofors anti-aircraft guns, 17 x 20 mm Oerlikon anti-aircraft cannons
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1932
- Crew: 848
The Portland class’s primary armament consisted of a series of 8-inch/.55 caliber guns mounted in triple turrets. Additionally, it was outfitted with an anti-aircraft defense system consisting of eight 5-inch/.25 caliber dual-purpose guns and a range of other smaller caliber machine guns.
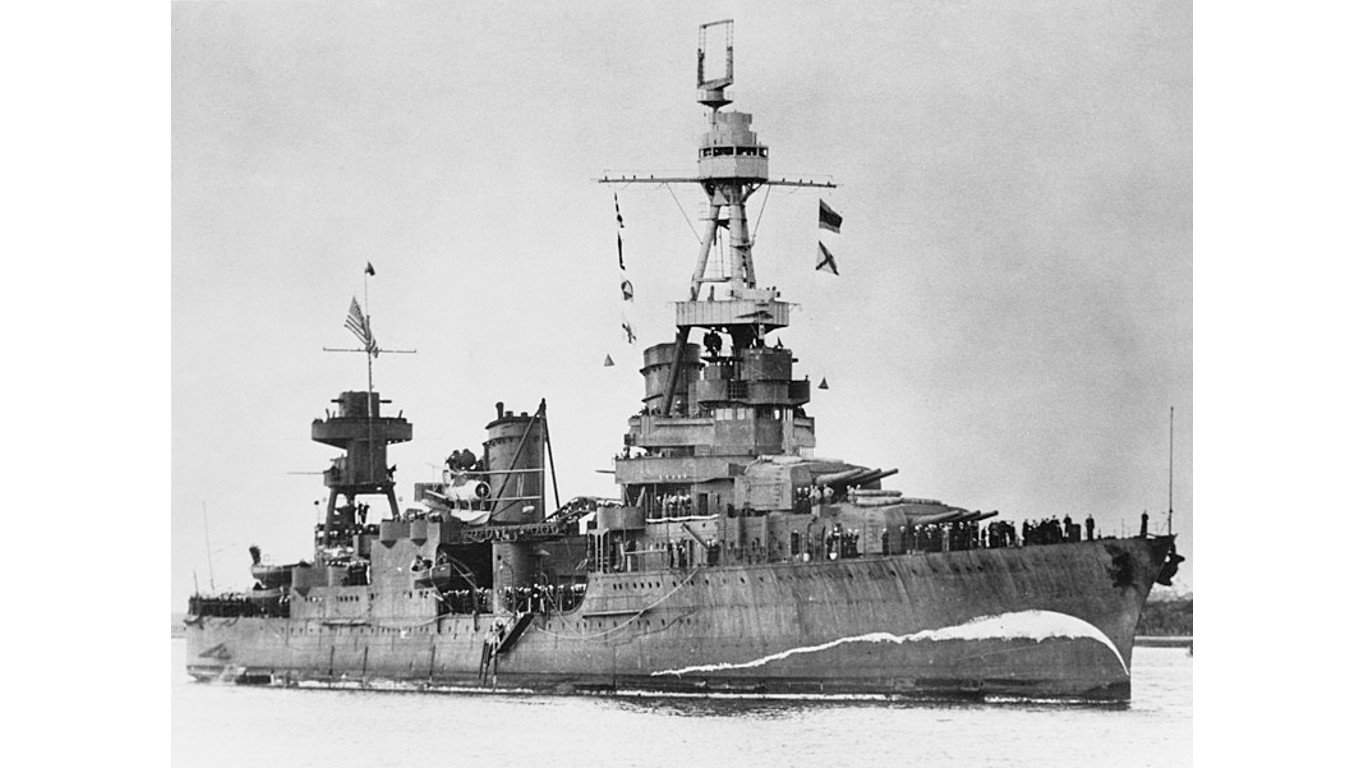
21. Northampton-class heavy cruiser

- Main armament: As built: 3 x 8 in/.55-cal triple guns, 4 x 5 in/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 6 x 21 in torpedo tubes; 1941: 3 x 8 in/.55-cal triple guns, 8 x 5 in/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 2 x 47 mm saluting guns, 4 x 1.1 in/.75-cal anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 6
- Launched: 1929
- Crew: 621
The Northampton-class heavy cruisers were equipped with nine 8-inch/.55 caliber rapid-fire naval guns arrayed in triple turrets, which allowed them to engage enemy vessels from a significant distance. At the same time, these warships featured anti-aircraft weaponry, which included four 5-inch/.25 caliber guns and various smaller caliber machine guns acted as a deterrent against enemy aerial threats.
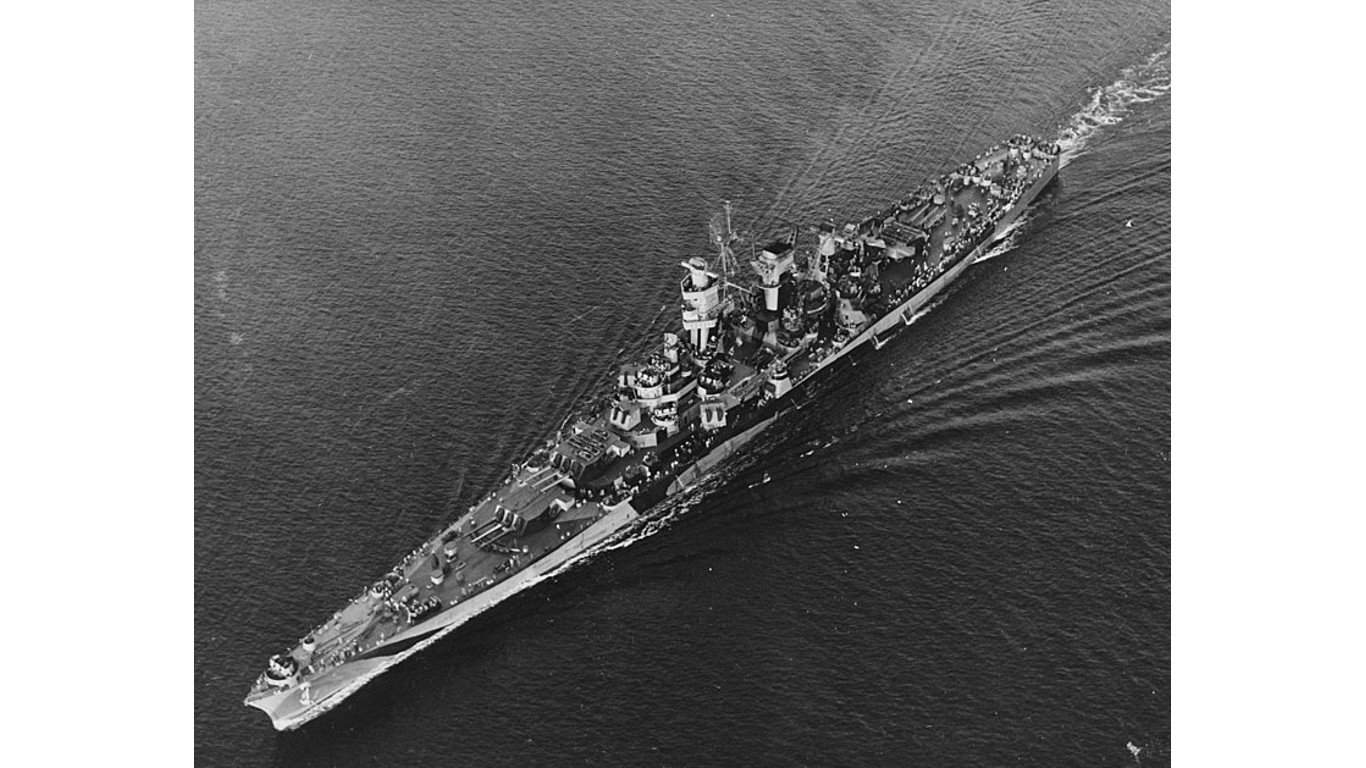
20. Alaska-class large cruiser

- Main armament: 9 x 305 mm guns, 12 x 127 mm dual purpose guns, 56 x 40 mm guns, 34 x 20 mm guns
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1943
- Crew: 2,251
The Alaska class was one of the most heavily armed U.S. Navy cruisers, with 200 mm-caliber cannons, some of the biggest at the time. The USS Alaska (CB-1) was key in covering the carriers Yorktown, Intrepid, Independence, and Langley as they advanced towards Japan in March 1945. Over the first month of this operation, the ship is credited with downing 12 Japanese aircraft.
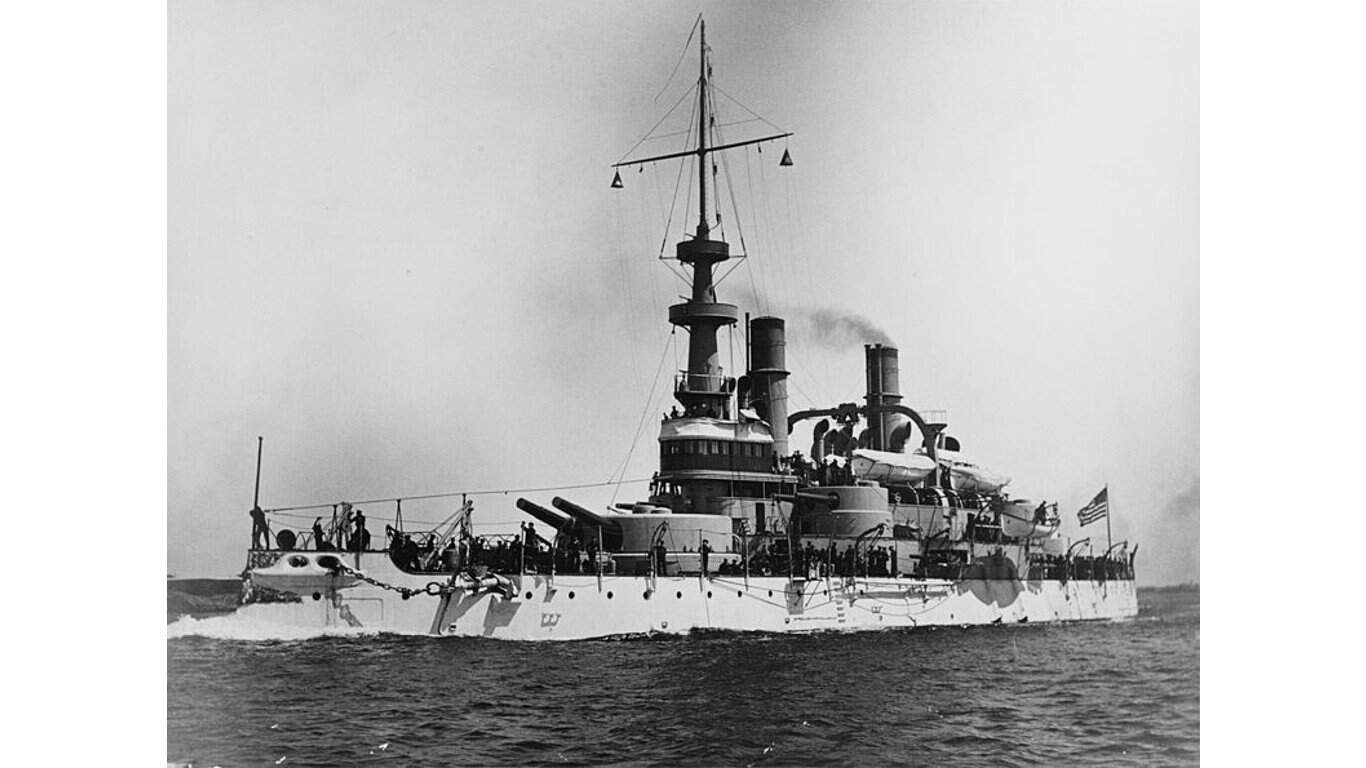
19. Indiana-class battleship

- Main armament: 4 x 13 in/.35-cal, 8 x 8 in/.35-cal, 4 x 6 in/.40-cal, two Colt gatling guns, 3 torpedo tubes
- Number built: 3
- Launched: 1893
- Crew: 473
The Indiana class is perhaps the oldest class of warships to participate in WWII—it was one of the United States’ first true battleship classes built before the turn of the 20th century. These ships’ main weapon was the four 13-inch/.35 caliber guns mounted on the hull, flanked by a series of lower-caliber guns and torpedo tubes.
The USS Oregon (BB-3) Indiana-class ship was nearly scrapped under the Washington Treaty but ultimately saved and later saw duty, primarily cargo transport, in WWII.
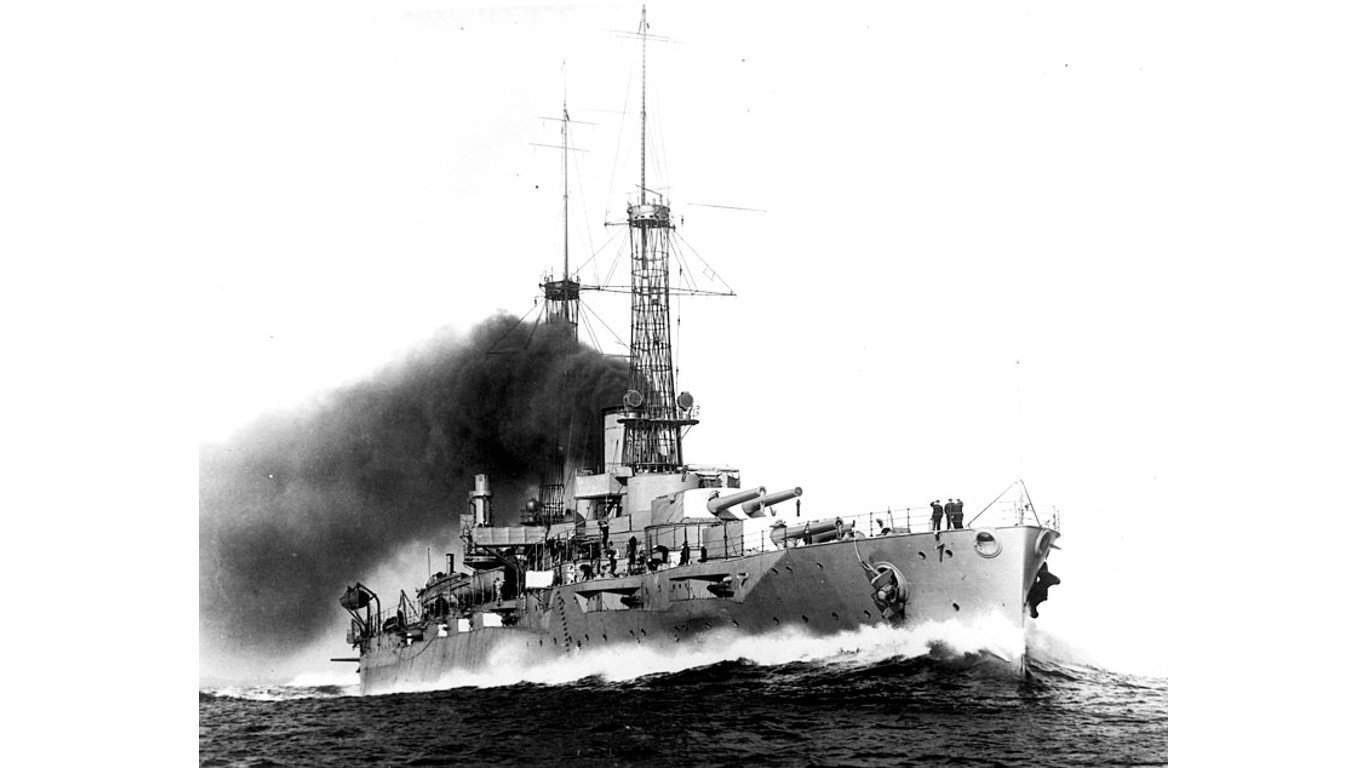
18. New York-class battleship

- Main armament: 5 x 14 in twin guns, 21 x 5 in single guns, 4 x 21 in torpedo tubes
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1912
- Crew: 1,042
The first New York-class battleship was built in 1912, and some of its weaponry lagged more current ships. Its primary armament consisted of 10 14-inch/.45 caliber guns, split into five twin-gun turrets. As secondary armament, these ships carried 21 5-inch/.51 caliber guns were versatile weapons for engaging smaller vessels and aircraft.
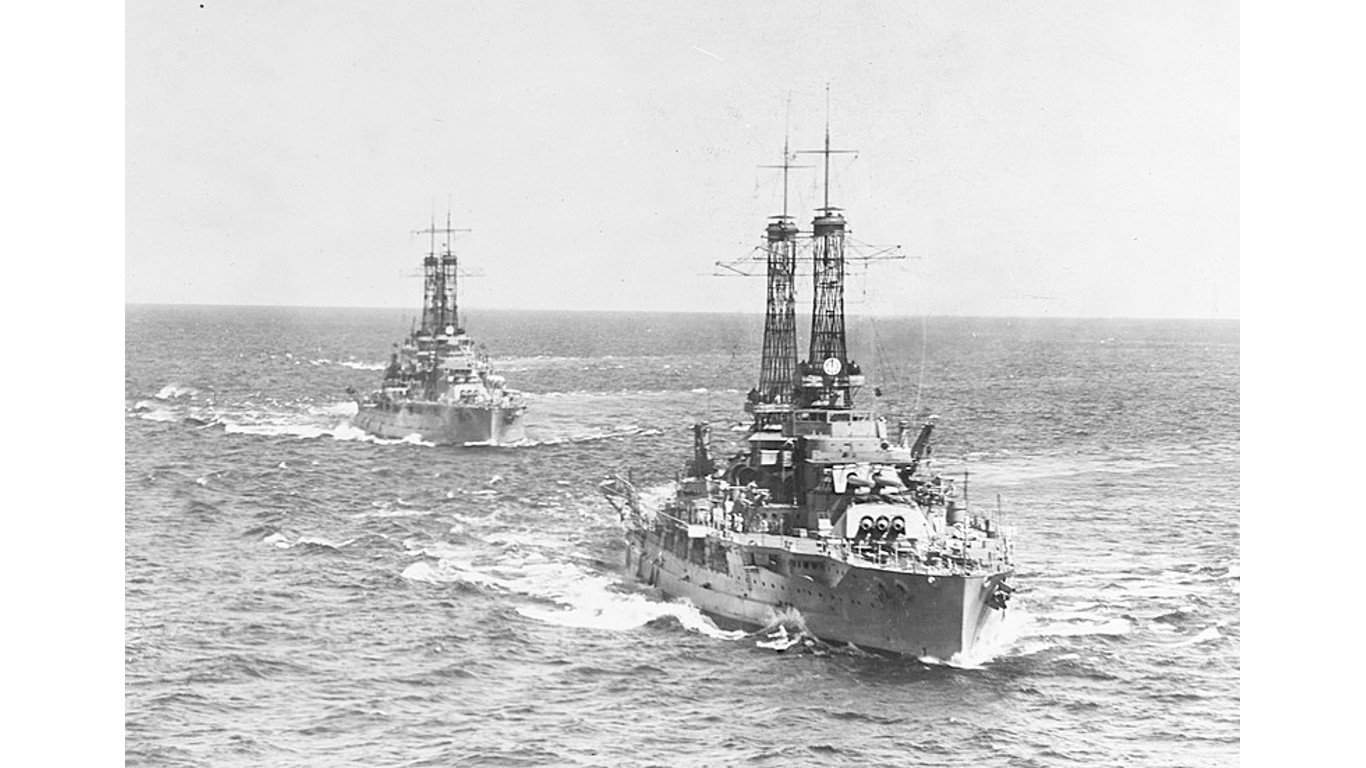
17. Nevada-class battleship

- Main armament: 10 x 14 in/.45-cal guns, 21 x 5 in/.51-cal guns, 4 x 21 in torpedo tubes
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1914
- Crew: 864
The Nevada-class battleships’ primary weaponry consisted of 10 14-inch/.45 caliber guns. These warships were equipped with 21 5-inch/for anti-aircraft and supplementary fire.51-caliber guns. These ships are considered some of the first “standard battleships” built in the era of WWI. One ship of the class was sunk in the Pearl Harbor bombing, and the other, though badly hit, would see action later in the war.
16. New Mexico-class battleship
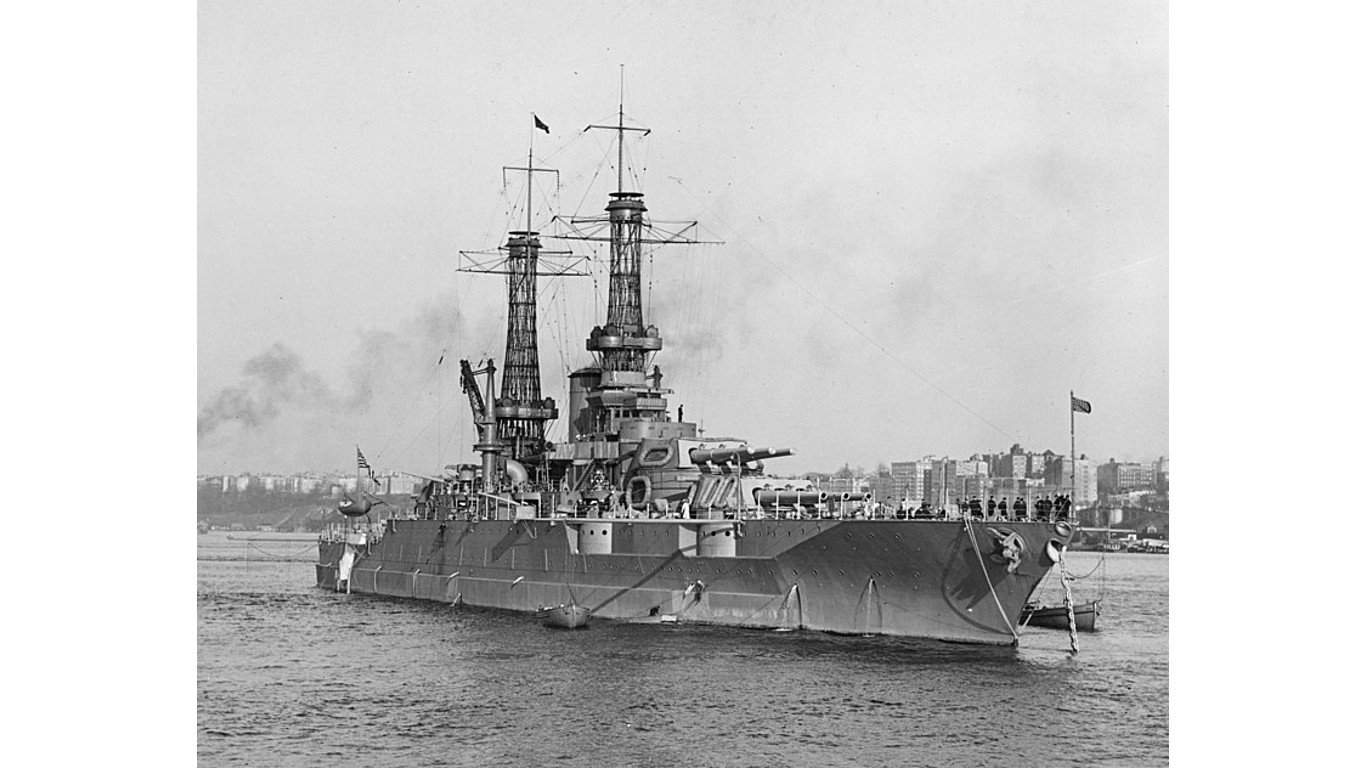

- Main armament: 12 x 14 in/.50-cal, 14 x 5 in/.51-cal, 2 x 21 in torpedo tubes
- Number built: 3
- Launched: 1917
- Crew: 1,084
The New Mexico-class battleships’ primary armament consisted of 12 14-inch/.50-caliber guns, strategically arranged in four triple turrets, delivering a powerful and concentrated barrage. Complementing the main armament, these warships featured 5-inch/.51-caliber secondary guns to defend against closer surface threats and torpedo boats.
These battleships were also equipped with various anti-aircraft guns and torpedoes to protect the fleet from aerial and underwater attacks.
15. Tennessee-class battleship
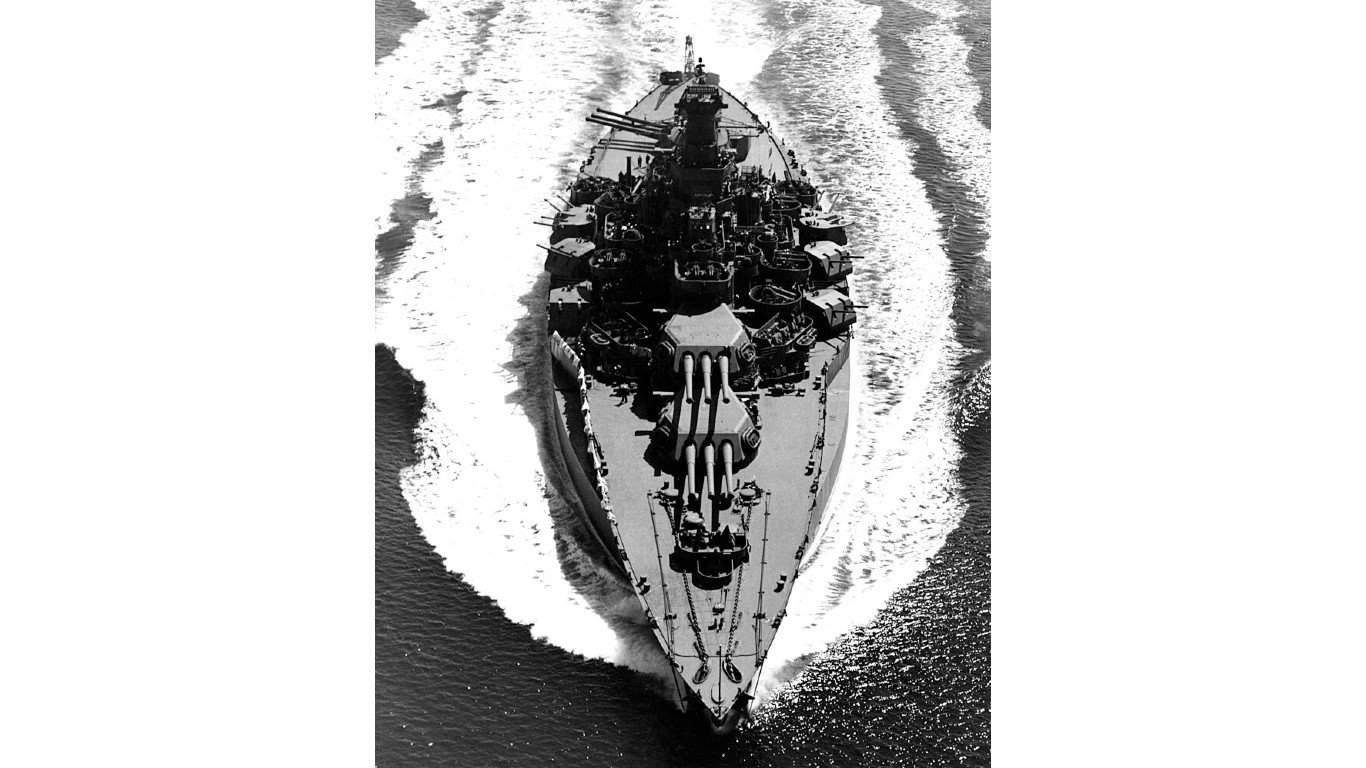

- Main armament: 4 x 14 in triple guns, 14 x 5 in single guns, 4 x 3 in single guns, 2 x 21 in torpedo tubes
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1919
- Crew: 1,083
The Tennessee-class battleships were equipped with 12 14-inch/.50 caliber guns as their primary armament, mounted in four triple-gun turrets. The USS Tennessee (BB-43) was the lead ship of this class of two and was present at the bombing of Pearl Harbor. It suffered some damage and needed a major overhaul.
However, the USS Tennessee would return with upgraded combat systems and sink the Japanese battleship Yamashiro in the Battle of Surigao Strait. The ship participated in the bombardment of Okinawa and was hit by a suicide plane but remained in action for almost another month before returning for more repairs.
14. Pennsylvania-class battleship
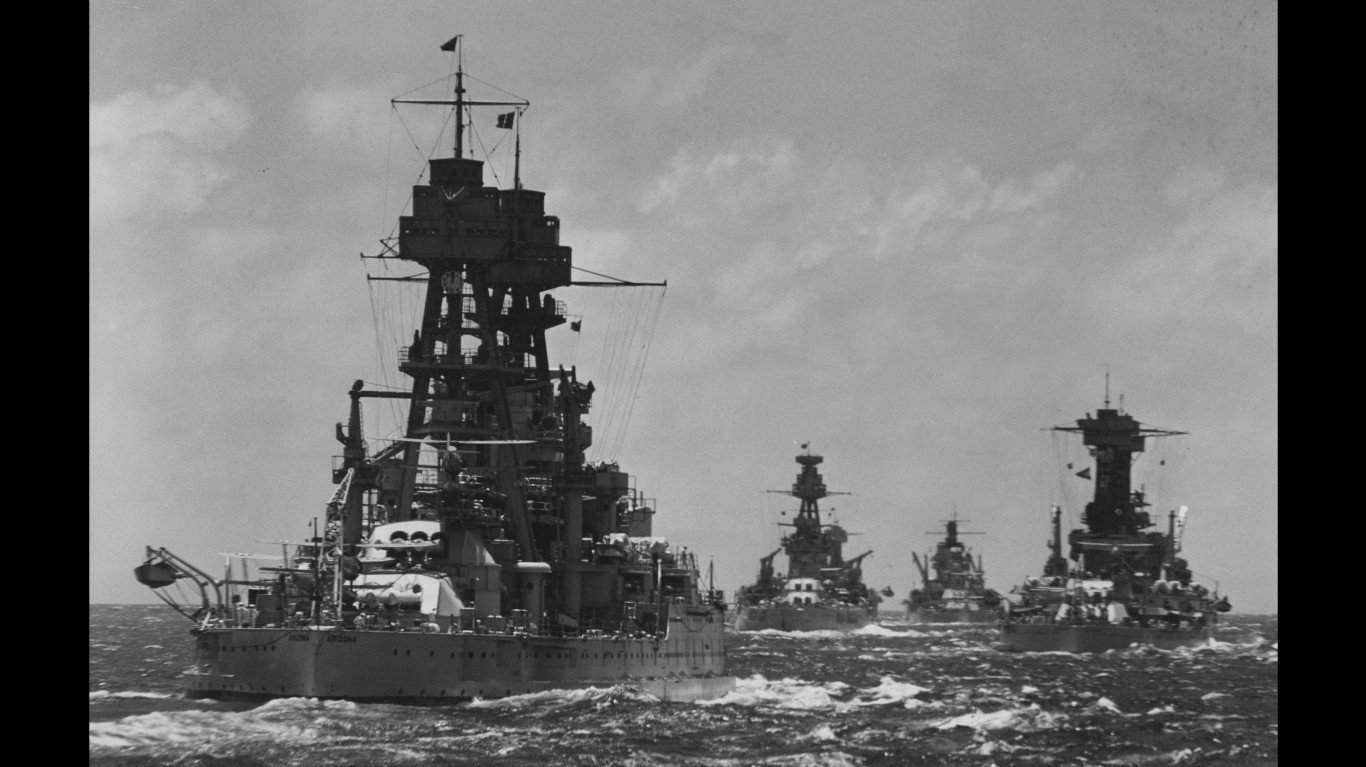

- Main armament: 4 x 360 mm/.45-cal triple guns, 12 x 130 mm/.51-cal guns, 12 x 130 mm/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 3 (tied)
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1915
- Crew: 915
The Pennsylvania-class battleships’ main battery consisted of 12 14-inch/.45 caliber guns arranged in four triple-gun turrets. Their secondary armament featured 5-inch/.51 caliber guns designed for quick firing against smaller vessels and airborne threats. This class was equipped with various anti-aircraft weapons, and over time, ships were retrofitted with advanced fire control systems to increase their striking power and defensive capabilities.
13. South Dakota-class battleship
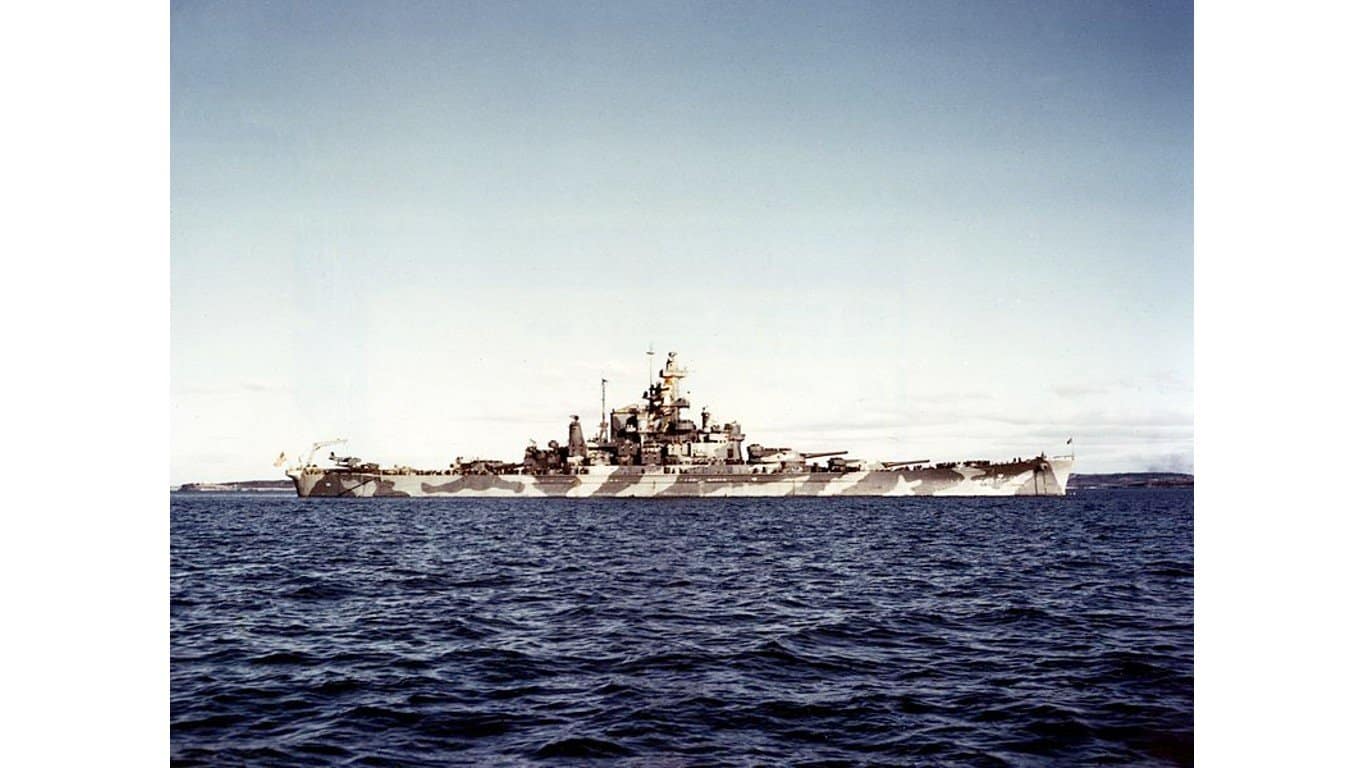

- Main armament: 9 x 406 mm/.45-cal Mark 6 guns, 16 x 127 mm/.38-cal DP guns, 68 x 40 mm guns, 76 x 20 mm guns
- Number built: 4 (tied)
- Launched: 1941
- Crew: 2,364
The South Dakota-class battleships were developed in the late 1930s and launched just in time for the war. Considering their later development, these warships were equipped with larger guns than previous generations of battleships.
This class was outfitted with nine 16-inch/.45 caliber Mark 6 guns in three triple turrets. Additionally, these vessels carried an array of anti-aircraft armaments, including 127 mm/.38 caliber guns, various smaller caliber weapons, and machine guns.
12. Colorado-class battleship
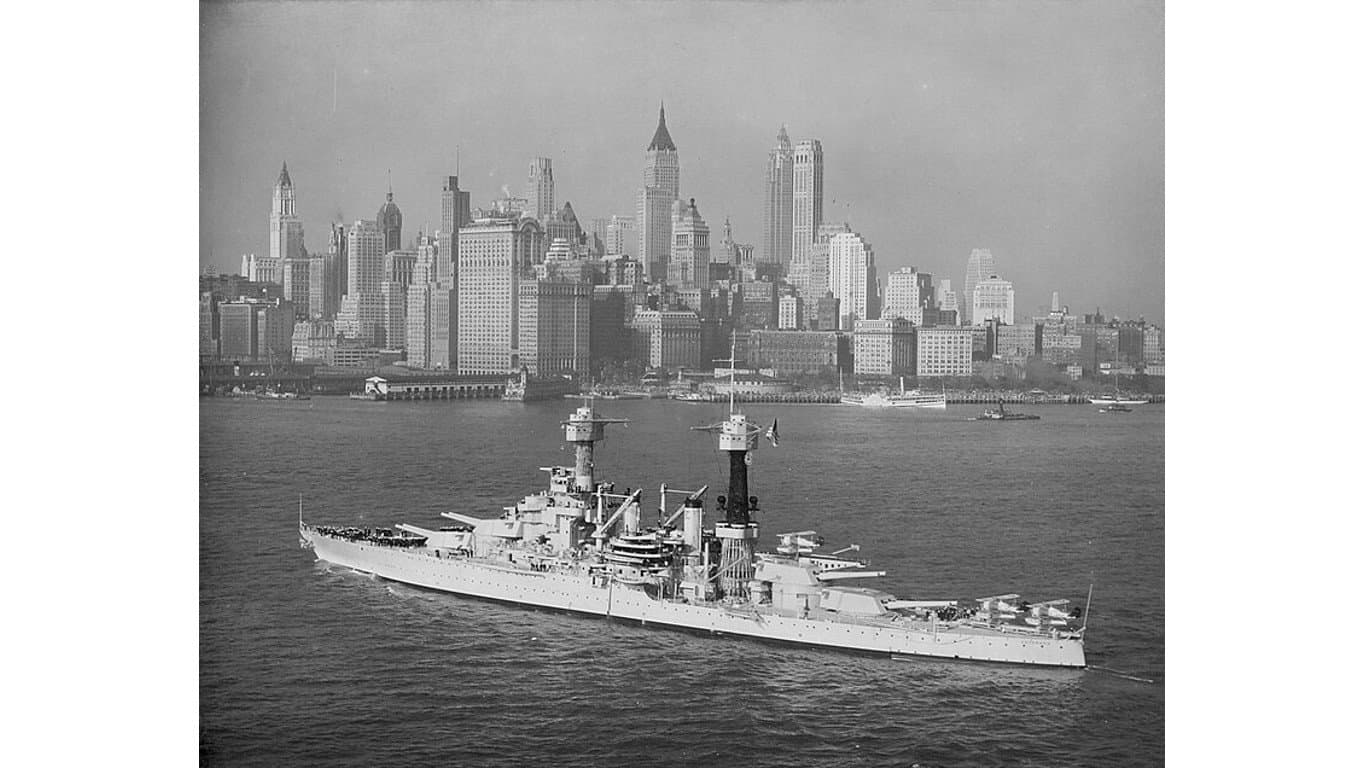

- Main armament: 8 x 16 in/.45-cal Mark 1 guns, 12 x 5 in/.51-cal guns, 4x3in/0.23-cal guns, 2x21in torpedo tubes
- Aircraft capacity: 4 (tied)
- Number built: 4
- Launched: 1920
- Crew: 1,080
The primary weaponry of the Colorado class consisted of 16-inch/.45 caliber guns. Complementing the primary guns were 5-inch/.51 caliber secondary guns were meant for combating smaller enemy vessels and weak points on enemy warships. This class was outfitted with an array of anti-aircraft weapons, providing some defense against close aerial threats and two torpedo tubes for dealing with other enemy vessels.
11. North Carolina-class battleship
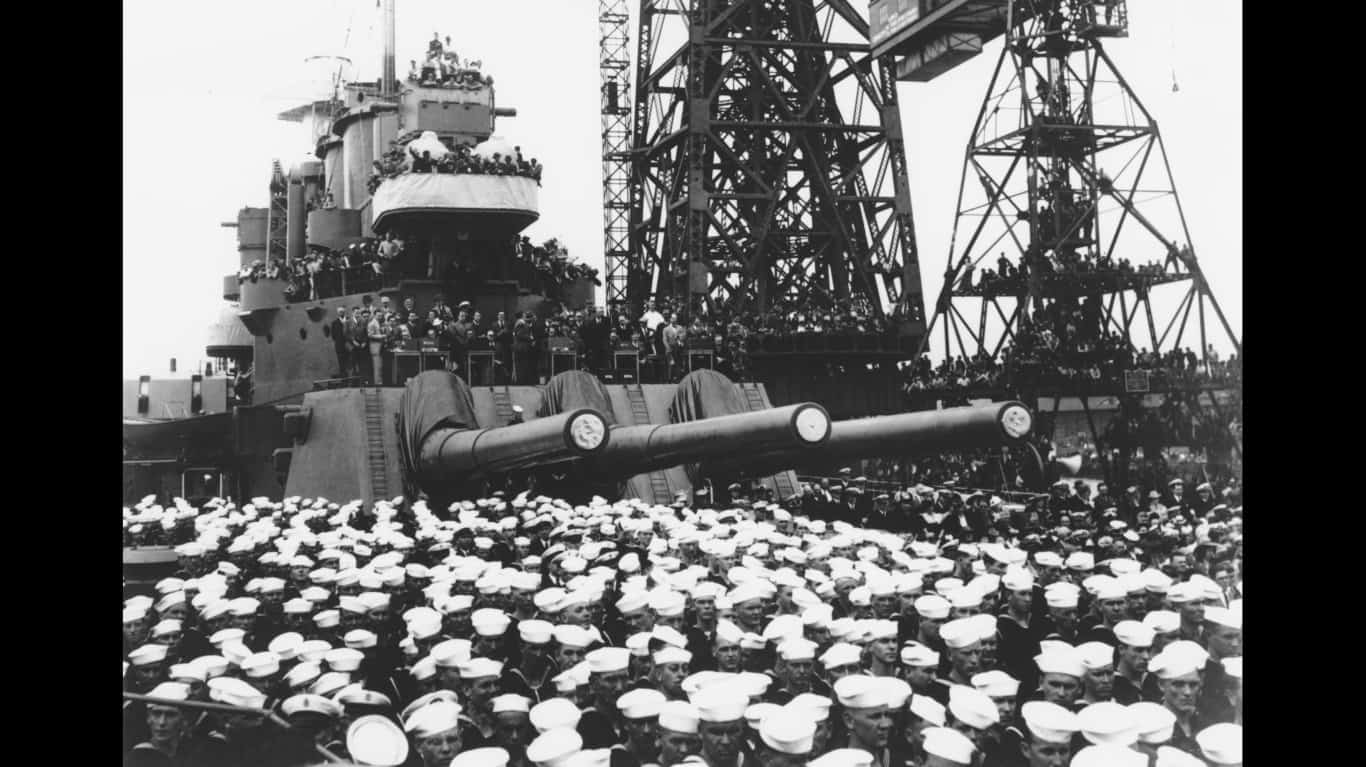

- Main armament: 9 x 16 in Mark 6 guns, 20 x 5 in/.38-cal guns, 16 x 1.1 in machine guns
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1940
- Crew: 1,880
The North Carolina-class battleships boasted an array of armaments that solidified their position as formidable warships. Their primary armament consisted of nine Mark 6 16-inch/.45-caliber guns as well as 5-inch/.38-caliber dual-purpose guns for anti-aircraft and surface engagement capabilities. There were a series of smaller caliber guns that served in defensive roles.
The USS North Carolina was the lead ship of its class and had an impressive service record throughout the war, recording 15 battle stars. Also, during the Battle of the Eastern Solomons, the ship is said to have shot down between seven and 14 Japanese aircraft.
10. Iowa-class battleship
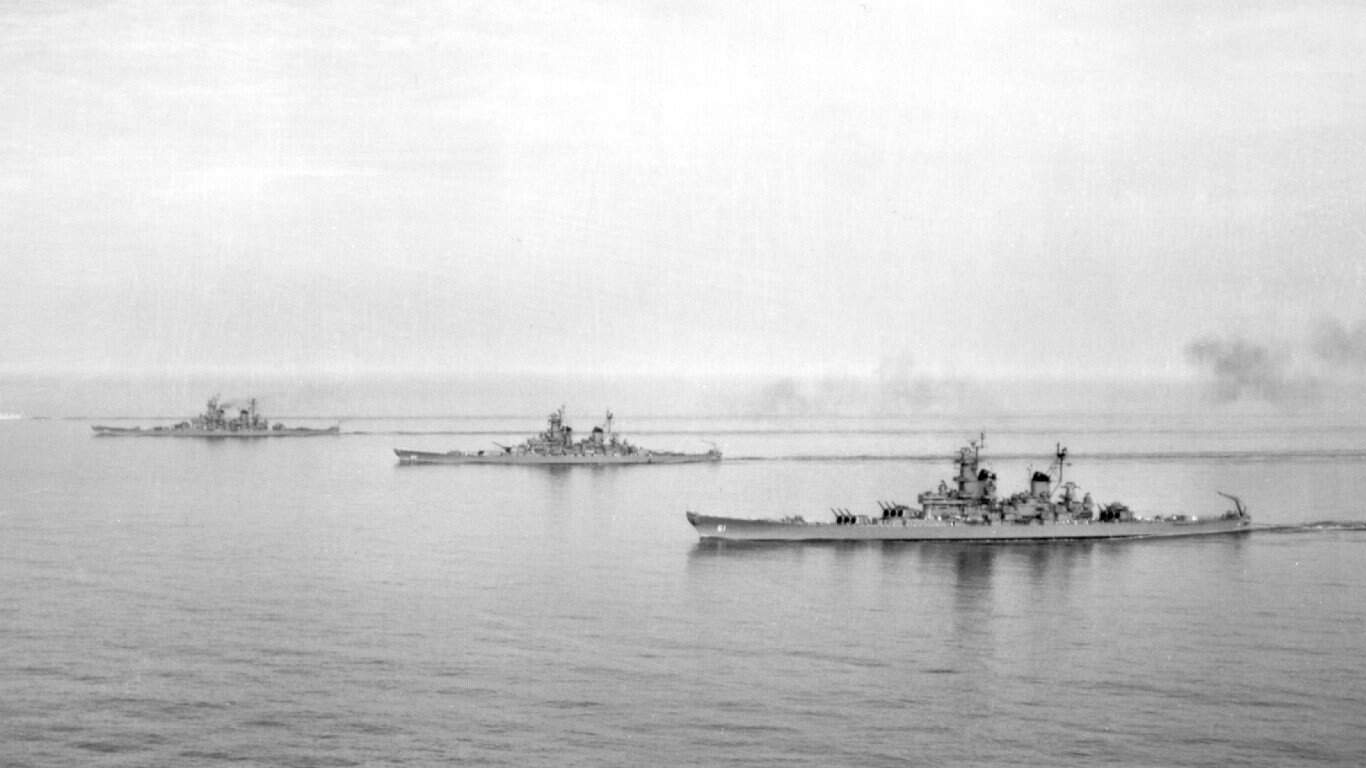

- Main armament: 3 x 16 in/.50-cal triple Mark 7 guns, 20 x 5 in/.38-cal Mark 12 guns, 80 x 40mm/.56-cal Bofors anti-aircraft guns, 49 x 20 mm/.70-cal Oerlikon anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 3 (tied)
- Number built: 4
- Launched: 1942
- Crew: 1,921
The Iowa-class battleships’ primary armament consisted of 16-inch/.50 caliber Mark 7 guns, capable of accurately firing 2,700-pound armor-piercing shells across distances up to 23 miles. This class also had a variety of secondary and anti-aircraft weaponry, including a combination of 40 mm Bofors anti-aircraft guns and 20mm Oerlikon cannons.
9. Long Island-class escort carrier
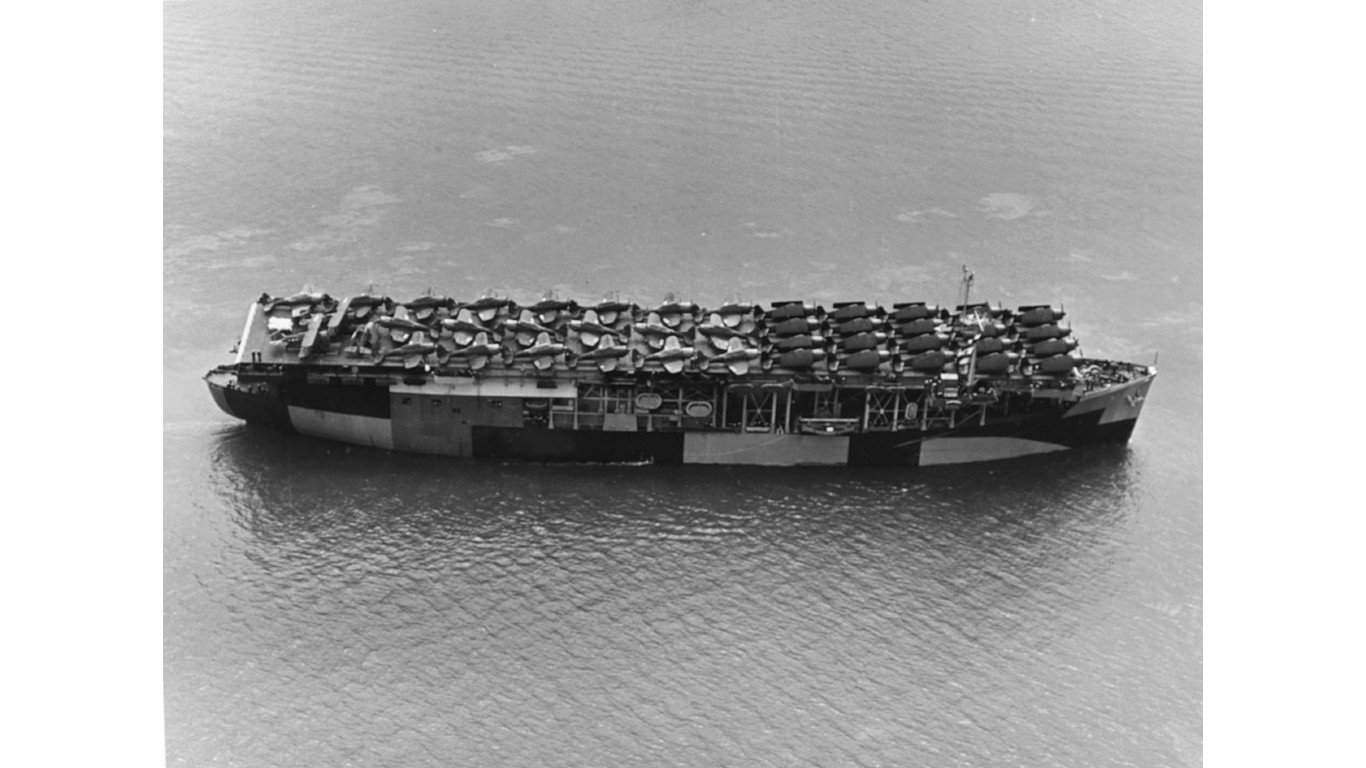

- Main armament: 1 x 5 in/.51-cal gun, 2 x 3 in/.50-cal gun
- Aircraft capacity: 21
- Number built: 1
- Launched: 1940
- Crew: 970
The Long Island-class escort carrier only had one ship within its class, the USS Long Island (CVE-1). As an aircraft carrier the armament for this ship was not especially impressive. However, the 21 aircraft this vessel could launch were capable of incredible damage with their payloads. As for the actual armament, the USS Long Island had a 5-inch/.51 caliber gun and two 2-inch/.50 caliber guns.
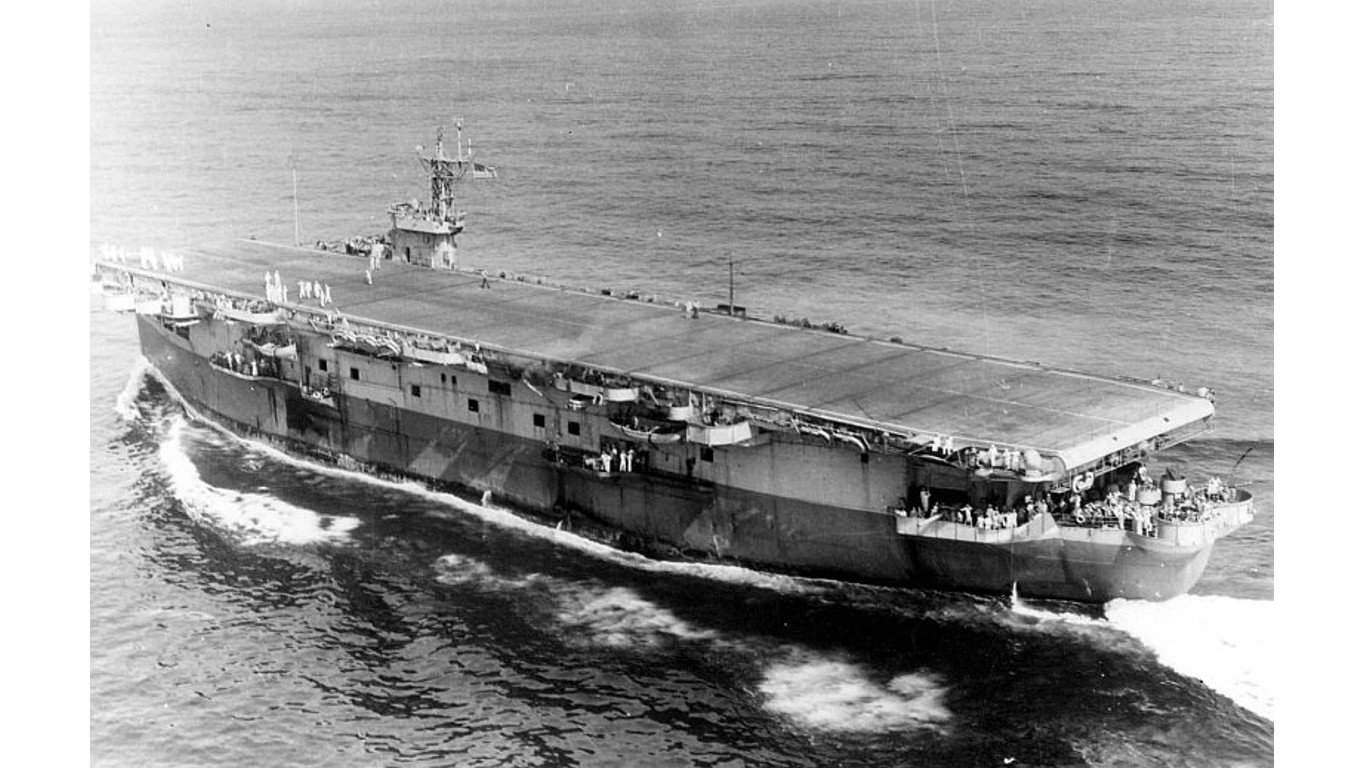
8. Bogue-class escort carrier

- Main armament: 1942: 2 x 5 in/.51-cal guns, 10 x 20 mm Oerlikon anti-aircraft cannons; 1945: 2 x 5 in/.38-cal guns, 8 x 40 mm twin Bofors anti-aircraft guns, 20 x 20 mm Oerlikon anti-aircraft cannon
- Aircraft capacity: 24
- Number built: 45
- Launched: 1941
- Crew: 890
The Bogue-class of escort carriers was headed by the USS Bogue (CVE-9), which played a critical role in the Hunter-Killer practice of hunting and destroying submarines. Along with a complement of high-caliber weapons and anti-aircraft cannons, the USS Bogue hosted 24 aircraft capable of spotting and bombing submarines.
Throughout the war, the USS Bogue sank a total of 10 German submarines and two Japanese submarines while reportedly damaging at least seven more submarines.
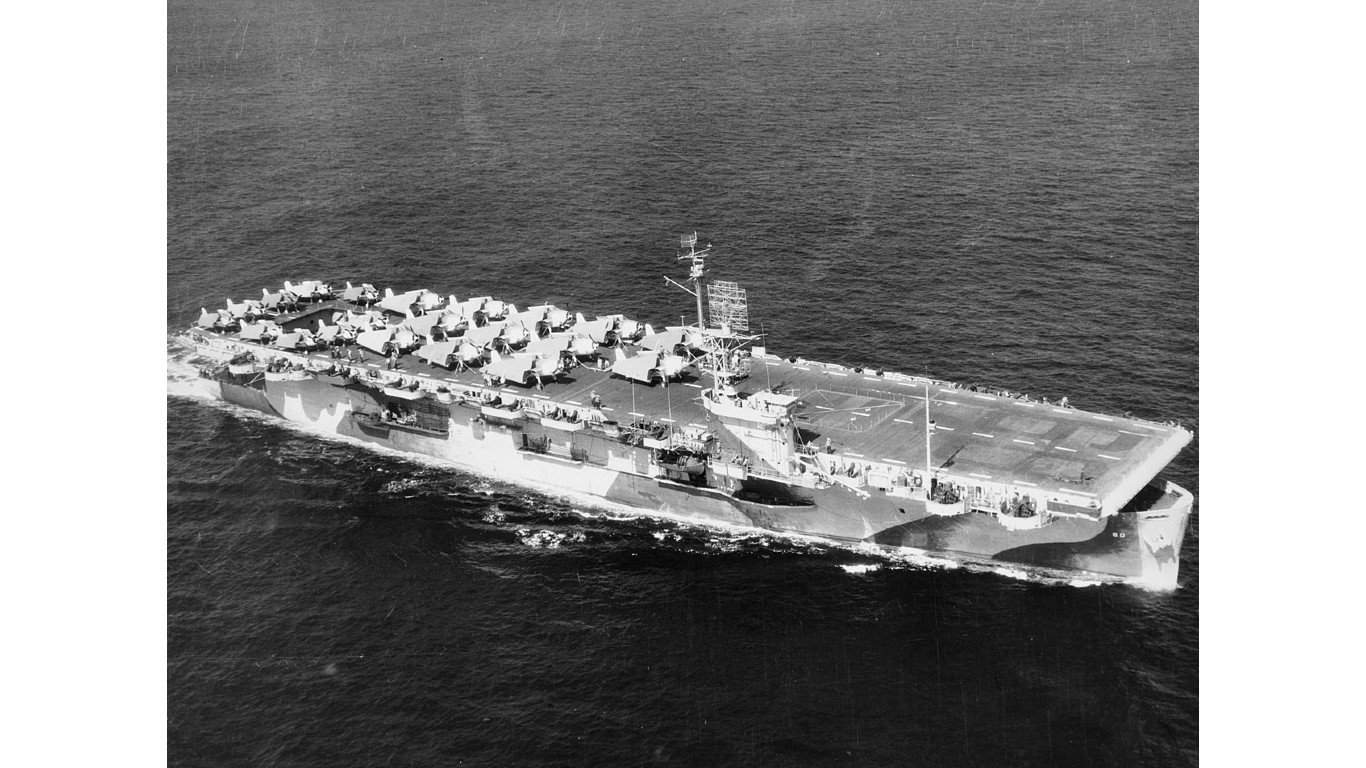
7. Casablanca-class escort carrier

- Main armament: 1 x 5 in/.38-cal DP gun, 8 x 40 mm twin Oerlikon cannons, 28 x 20 mm Bofors anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 28
- Number built: 50
- Launched:1943
- Crew: 860
The Casablanca class was WWII’s most widely produced escort carrier, with 50 entering the service. The primary armament was a 5-inch/.38 caliber gun, flanked by 40 mm Oerlikon cannons and 20 mm Bofors anti-aircraft guns, provided aerial defense in intermediate and close ranges. These escort carriers could host 28 aircraft, commonly Grumman F4F Wildcats or Hellcats.
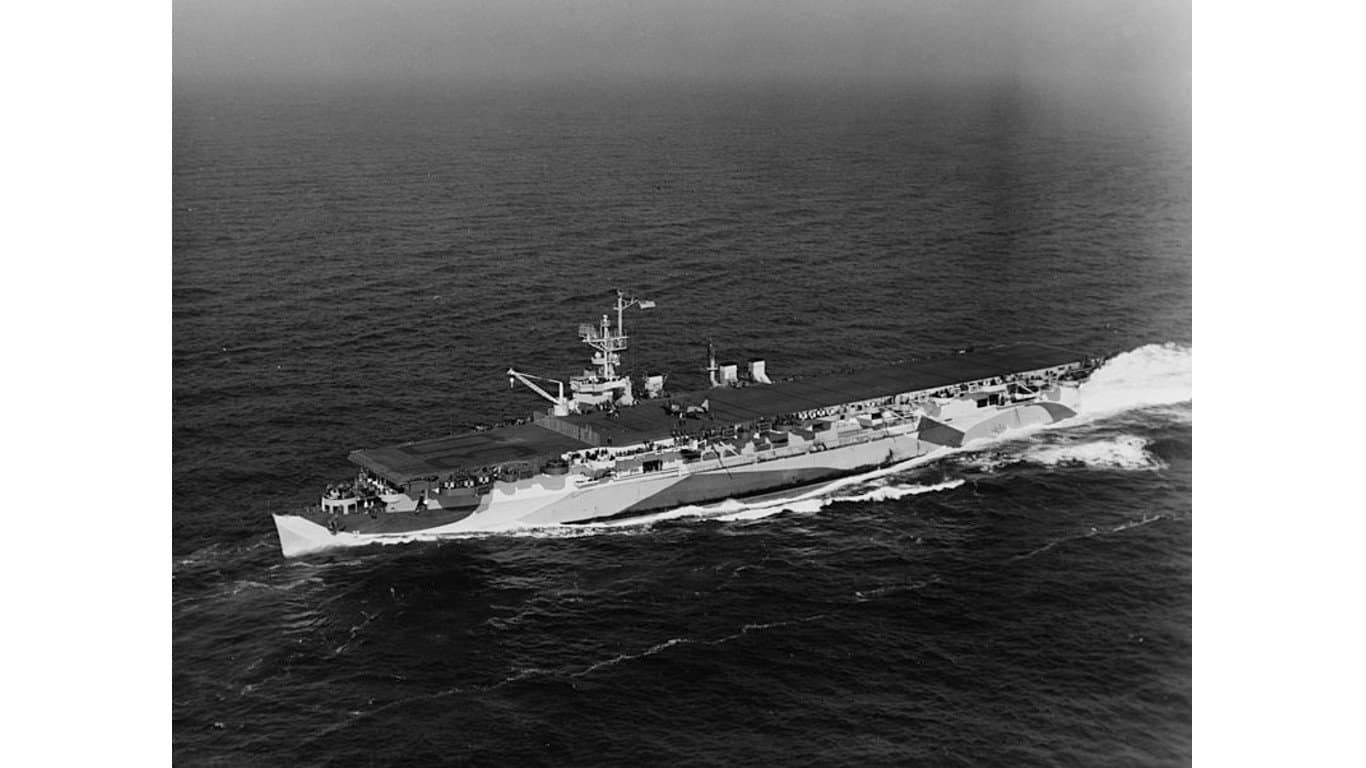
6. Independence-class light carrier

- Main armament: 24 x 40 mm Bofors guns, 22 x 20 mm anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 30
- Number built: 9
- Launched: 1942
- Crew: 1,569
The Independence-class aircraft carriers were introduced in the later years of WWII. Like most aircraft carriers, they were not heavily armed, but their destructive capability lay with the aircraft they hosted.
Their air wings, composed of fighter, bomber, and torpedo aircraft, delivered powerful airborne firepower across land and sea. Additionally, these carriers were equipped with anti-aircraft guns, such as the 40 mm Bofors, which provided reliable protection against aerial threats.
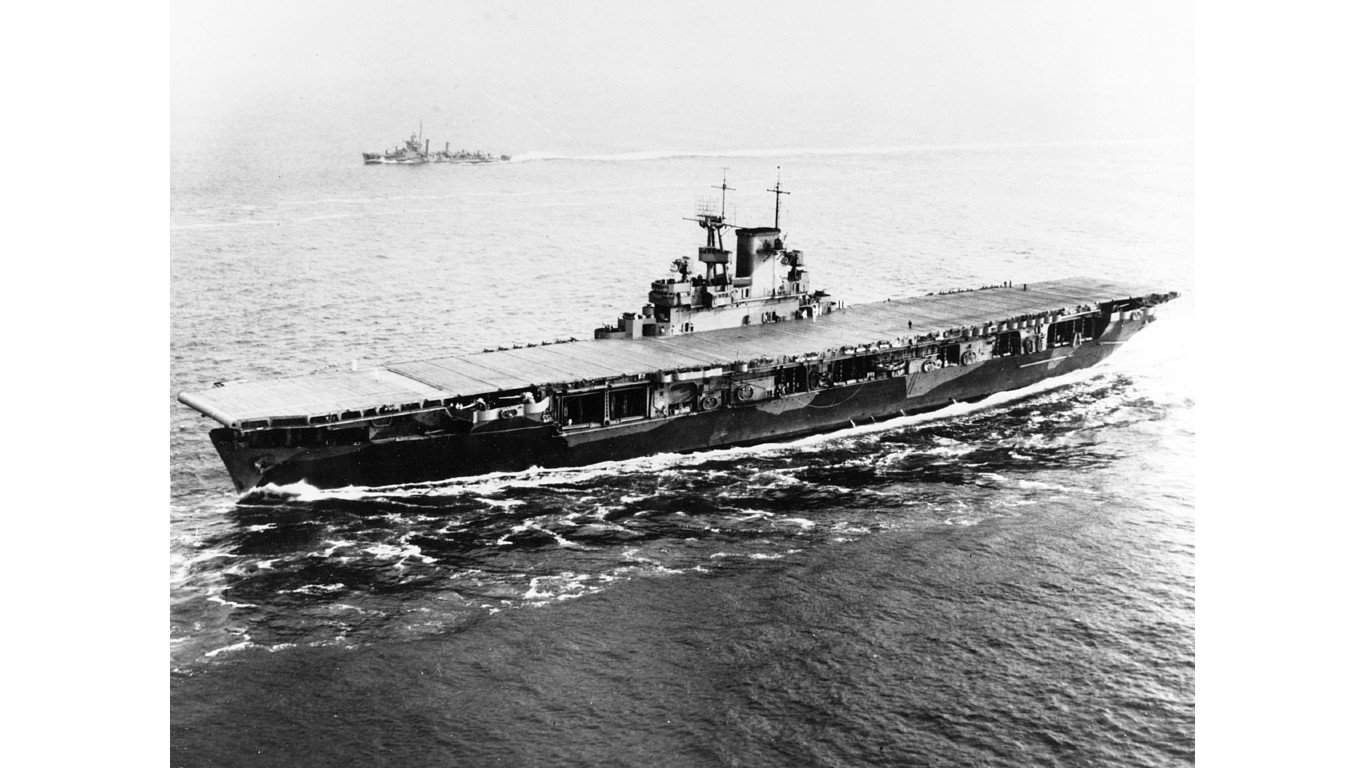
5. Wasp-class aircraft carrier

- Main armament: 8 x 5 in/.25-cal guns, 4 x 1.1 in anti-aircraft guns, 24 x .50-cal machine guns
- Aircraft capacity: 80
- Number built: 1
- Launched: 1939
- Crew: 1,800
The Wasp-class aircraft carriers had only one ship, the USS Wasp (CV-7). The primary guns on this aircraft carrier included eight 5-inch/.25 caliber guns, four 1.1-inch anti-aircraft guns, and 24 .50 caliber machine guns.
The USS Wasp was home to 80 aircraft, including fighters, bombers, and more. However, it was sunk in the Battle of Guadalcanal and did not survive the war. The ship was awarded two battle stars.
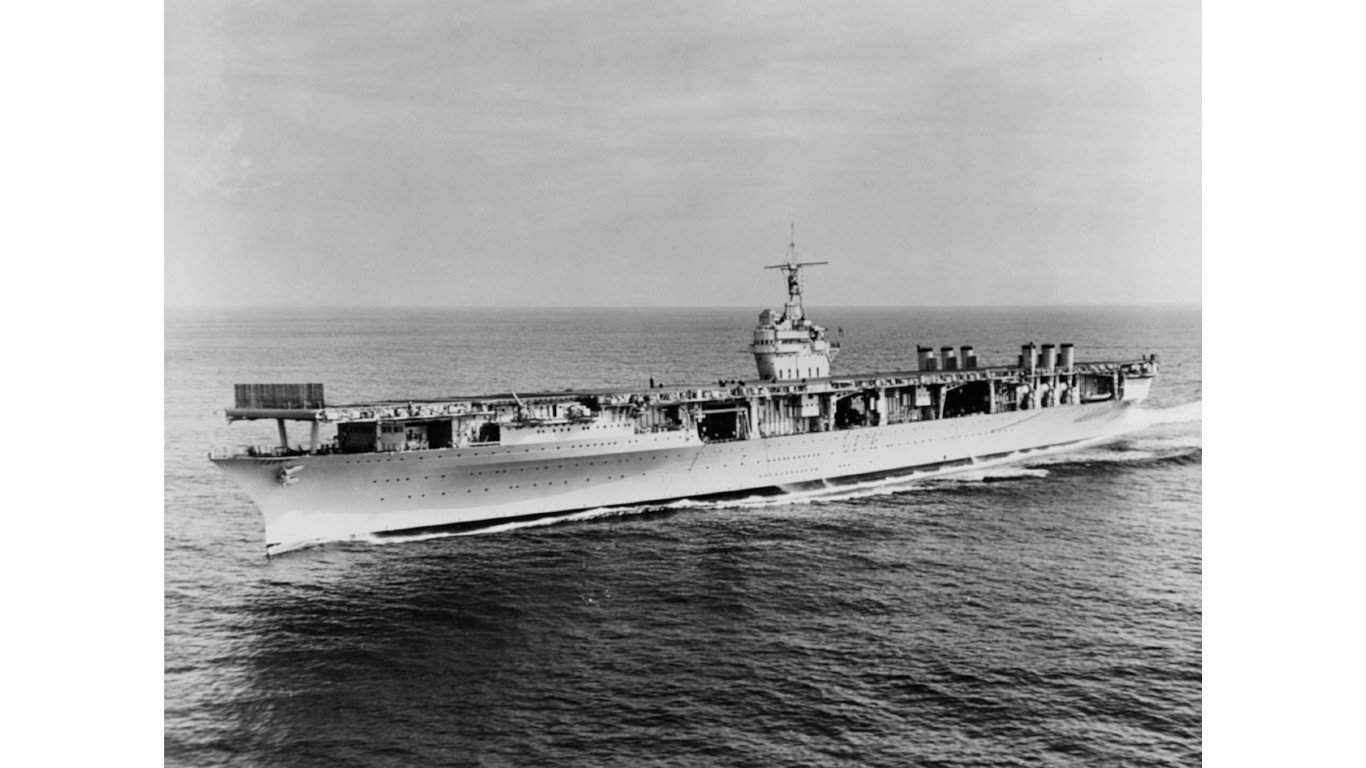
4. Ranger-class aircraft carrier

- Main armament: 8 x 5 in/.25-cal anti-aircraft guns, 40 x .50-cal machine guns
- Aircraft capacity: 86
- Number built: 1
- Launched: 1933
- Crew: 2,461
The USS Ranger (CV-4) is the only aircraft carrier of its class and was host to 86 aircraft. Like many other aircraft carriers, the USS Ranger relied on other ships for the big guns. Its armament was relatively weaker compared to cruiser or battleship classes.
The primary weapons on the USS Ranger were a series of eight 5-inch/.25 caliber guns, flanked by forty .50-caliber machine guns. While this carrier was not as celebrated as other classes, it still earned two battle stars throughout the war.
3. Essex-class aircraft carrier

- Main armament: 4 x 5 in/.38-cal twin guns, 4 x 5 in/.38-cal singe guns, 8 x 1.6 in/.56-cal quad guns, 46 x 0.8 in/.78-cal anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 90 (tied)
- Number built: 24
- Launched: 1942
- Crew: 2,600
The Essex-class was an iconic group of aircraft carriers vital to the United States Navy during WWII. The primary anti-aircraft weaponry consisted of 12 5-inch/.38 caliber twin guns placed strategically around the ship to provide maximum coverage.
Additionally, the Essex class carriers hosted a complement of 90 aircraft. The lead ship of this class, the USS Essex, played a vital role in the landings at Iwo Jima and the campaign against Okinawa.
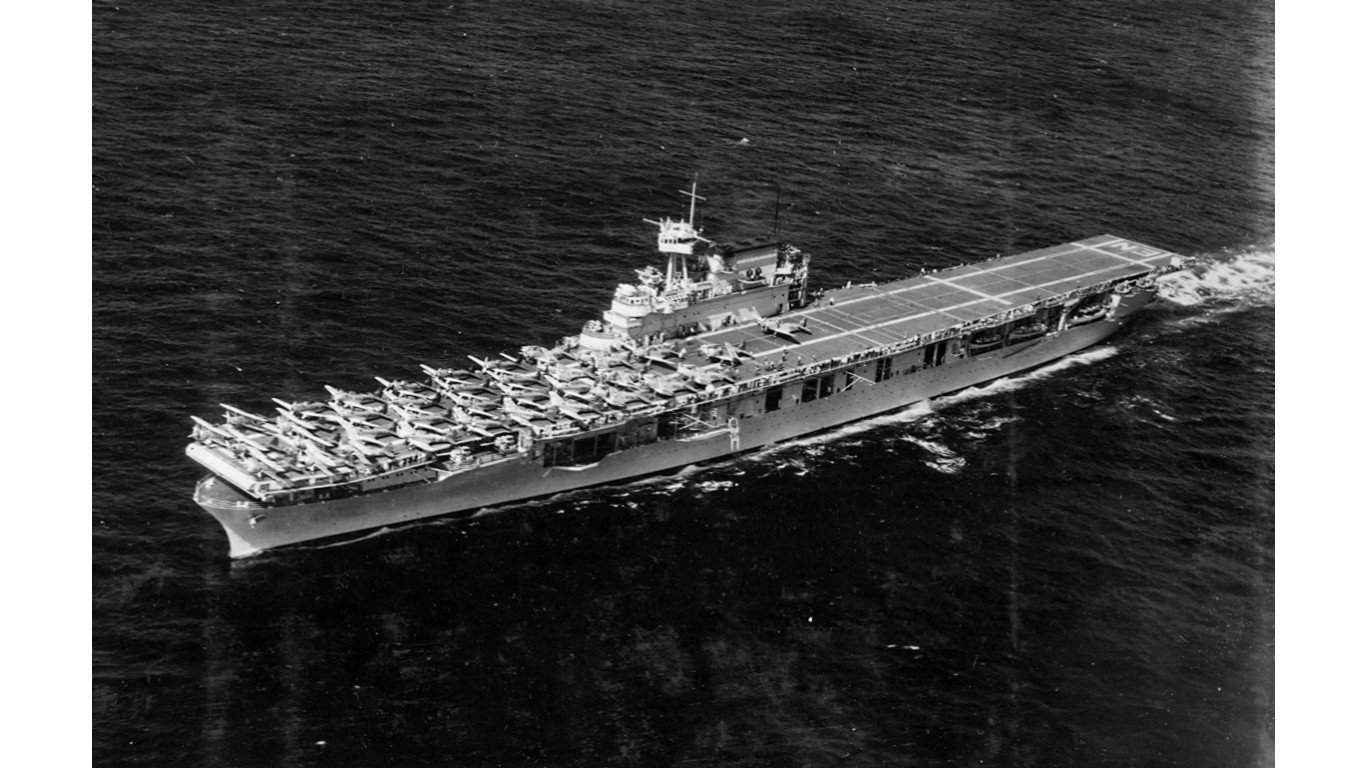
2. Yorktown-class aircraft carrier

- Main armament: 8 x 5 in/.38-cal guns, 4 x 1.1 in/.75-cal machine guns, 24 x .50-cal machine guns
- Aircraft capacity: 90 (tied)
- Number built: 3
- Launched: 1936
- Crew: 2,217
Like the other carriers on this list, the Yorktown-class aircraft carriers relied predominantly on their aircraft fleet rather than their physical armaments. Still, these vessels were armed with dual-purpose 5-inch/.38 caliber guns, complemented by a series of 1.1-inch/.75 caliber machine guns serving in an anti-aircraft role.
As the war progressed, the carriers saw upgrades to their anti-aircraft arsenal, adding 20 mm Oerlikon and 40 mm Bofors anti-aircraft guns, enhancing their capabilities to defend against rapidly evolving aerial threats. The USS Enterprise (CV-6) is perhaps the most famous carrier in this class, boasting the most battle stars of any vessel in WWII.
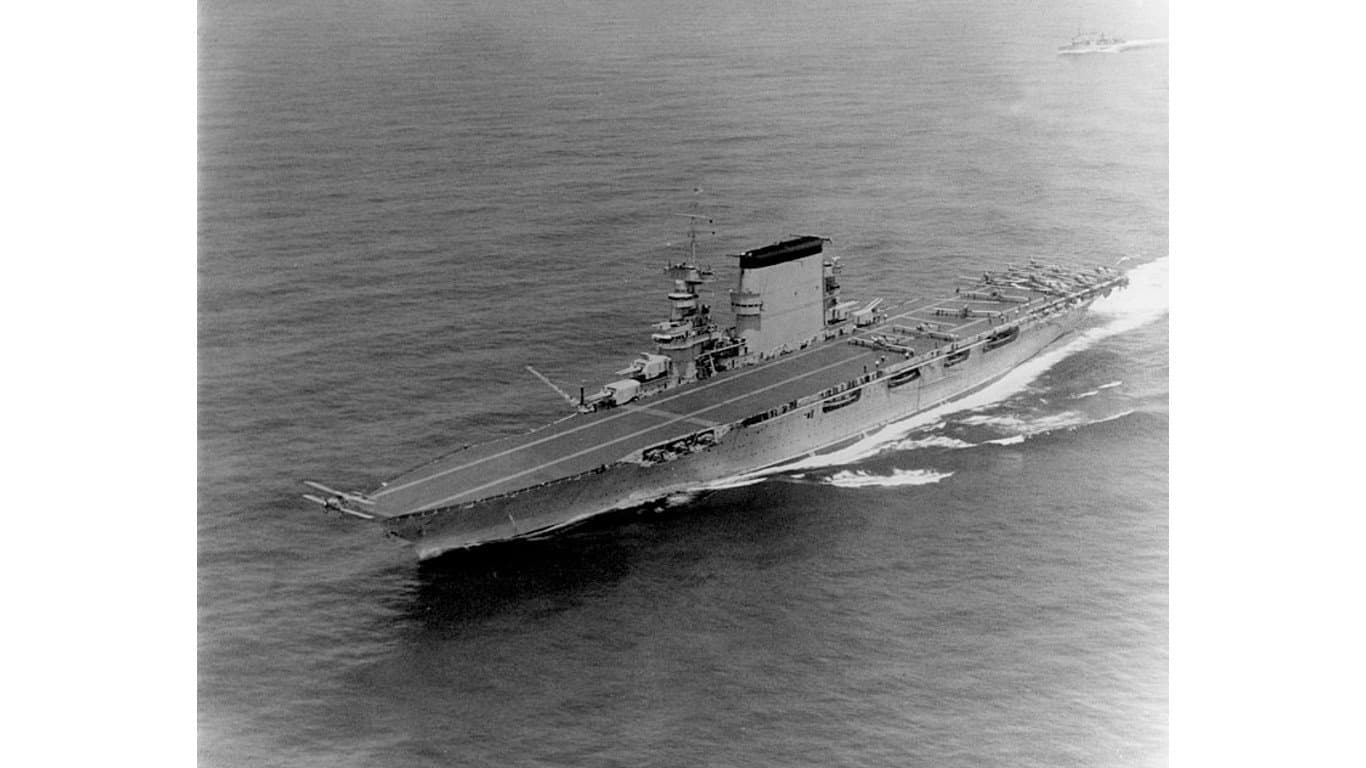
1. Lexington-class aircraft carrier

- Main armament: 4 x 8 in/.55-cal twin guns, 12 x 5 in anti-aircraft guns
- Aircraft capacity: 91
- Number built: 2
- Launched: 1925
- Crew: 2,122
The Lexington-class aircraft carriers were some of the largest in the U.S. Navy by crew, with several aircraft at 90 in size. These carriers were designed with four 8-inch/.55 caliber twin guns and lower caliber anti-aircraft guns. Lexington-class ships were originally designed as battlecruisers in the early 1920s but were later outfitted as aircraft carriers.
The lead ship of this class, the USS Lexington, played a key role in the Battle of Coral Sea. Its air group scored the first sinking of the battle, destroying the Japanese ship Shoho. However, the ship would not survive the war, as it was sunk in May 1942.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Public Domain / Wikimedia Commons.



