If you thought that a large battery was the one in your car, you need to think again! Battery technology is remarkably scalable, meaning that you can have batteries the size of football stadiums, supplying power to the grid.
The technology used to create the largest batteries on Earth has really sped up over the last decade, with companies like Tesla building expansive battery installations that are maximizing the utility of renewable energy sources and making power cleaner and more cost-effective for consumers.
Read on for an informative profile of the world’s biggest batteries and the essential role they play in providing clean and consistent power for industry and consumers, spanning a range of locations and technologies.
1. The Edwards & Sanborn Solar Plus Storage Project
- Location: Kern County, California
- Capacity: 875MW/3,287MWh
- Launched: 2001
- Developers/Stakeholders: Terra-Gen
The largest battery storage system on Earth currently resides in California on 4,600 acres of land. It’s a project of Terra-Gen, a familiar company in the industry that operates four energy storage systems in California.
The Edwards & Sanbord Solar Plus Storage Project began in 2021 and now consists of 1.9 million modules from First Solar. It can produce and store more energy than any site on earth thanks to 875MWdc of solar PV and 3,287 MWH hours of BESS capacity. Samsung, LG Chem, and BYD are responsible for the 120,000+ batteries in the company’s array.
While located in Kern, Country California, part of the project is on Edwards Air Force Base and private land. The second phase of this massive undertaking came online in early 2024 and provides power to more than ten customers in the area, including Southern California Edison and Pacifica Gas & Electric.
2. The Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility
- Location: Moss Landing, Monterey County, California, United States
- Capacity: 750 MW/3,000 MWh
- Launched: December 2020
- Developers/Stakeholders: Vistra Energy Corporation, Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E)
The Energy Storage Facility at Moss Landing is one of the world’s largest online grid-scale batteries. It was built in three phases, with Phase I being a 300 megawatts/1,200 megawatt-hours battery.
Phase II, completed in 2021, added an additional 100 MW/400 MWh for a total capacity of 400 MW/1,600 MWh. In late 2023, Phase III allowed this facility to produce 750 MW and 3,000 MWh. The Vistra Energy Corporation owns this plant. The regional energy company has invested in this energy storage infrastructure to support a transition to cleaner energy resources.
Vistra expects the Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) to serve as a model for battery storage in the U.S. in the coming decades. Phase I of this project utilizes more than 4,500 individual batteries stacked in racks of 22 battery modules.
These battery modules capture unused energy from the grid, particularly solar energy. They will automatically release the accumulated power when demand is high, during peak periods, like morning and early evenings. This giant battery serves Pacific Gas and Electric Company on a long-term contract.

3. The Dalian Flow Battery Energy Storage Peak-Shaving Power Station
- Location: Shahekou District, Dalian, Liaoning Province, People’s Republic of China
- Capacity: 100 MW/400 MWh (currently), 200 MW/800 MWh (total)
- Launched: 2022
- Developers/Stakeholders: Dalian Rongke Energy Storage Technology Development Co Ltd, the Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Dalian battery farm in Liaoning Province is one of the world’s largest batteries and is almost certainly the largest non-Lithium battery on Earth. It uses flow battery energy technology, a new battery technology that combines tanks of electrolytes to generate electrical current, rather than using the more widely adopted lithium-ion technology.
The facility in northeast China took six years to build at a cost of 1.9 billion yuan ($267 million) and has a current capacity of 100 MW/400 MWh. This mega battery has just come online, and once operating, the capacity is expected to be further increased to 200 MW/800 MWh.
The massive battery farm will help the region manage peaks and troughs in its electricity supply. It will also increase the use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. The Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, suggests that it will be able to supply the energy requirements of over 200,000 households.
4. Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E) Battery Energy Storage (BESS) Elkhorn Battery Project
- Location: Moss Landing, Monterey, California
- Capacity: 182.5 MW /730 MWh
- Launched: 2021
- Developers/Stakeholders: Tesla, Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E), California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC)
The Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E) Battery Energy Storage (ESS) Project in Moss Landing is a mega battery facility that can store and release up to 182.5 MW of power to the grid, with 730 MWh of capacity. This is the equivalent of 7,300 electric cars, each with a 100 kWh battery.
PG&E expects the battery energy storage facility to save as much as $100 million over the next 20 years by supporting local demand and reducing energy procurement costs.
This mega battery is one of four approved by authorities in Monterey County and utilized by PG&E. It is made up of 256 Tesla Megapacks, each with a capacity of 3 MW. The Megapacks are lithium-ion batteries on concrete slabs.
Tesla and PG&E designed and developed the facility and completed it in early 2021, with full commercial operation commencing later the same year. According to the commercial agreement between Tesla and PG&E, the site’s capacity can expand to as much as 1.1 GWh.
5. The Victorian Big Battery
- Location: Moorabool Terminal Station, Geelong, Australia
- Capacity: 300 MW / 450 MWh
- Launched: 2021
- Developers/Stakeholders: Tesla, Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO), the Victorian Government, Neoen, AusNet Services
On the outskirts of Geelong, a Victorian city about 65 km (40 mi) from Melbourne, is a grid-scale battery storage facility with a capacity of over 300 MW. The Victorian Big Battery (VBB) is a massive development covering an area the size of an Aussie rules football stadium. It can store enough energy to power over one million homes for at least 30 minutes. The VBB began operating on November 21st, 2021.
Over 200 Tesla Megapacks comprise this array. Tesla has partnered with the owner and operator of the VBB, Neoen, a renewable energy company. These are industrial lithium-ion batteries that provide grid-scale energy storage. Tesla has designed these batteries as individual modules equipped with:
- Bidirectional inverters
- Thermal management technology
- AC main breaker
- Individual controls
The Megapacks can be installed and scaled quickly. In combination, they’ve created the world’s first big battery. Victoria has installed this massive battery to help support a transition to renewable energy sources. Their goal is to use renewable energy sources for at least 50% of Victoria’s power by 2030.
These batteries will supply at least 250MW of peak capacity to support the regional electricity grid. The batteries are configured to automatically provide power in the event of a sudden network outage, supporting the grid’s stability.

6. The Hornsdale Power Reserve
- Location: Jamestown, South Australia, Australia
- Capacity: 150 MW / 193.5 MWh
- Launched: 2017
- Developers/Stakeholders: Tesla, Neoen, the South Australian Government, the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the Clean Energy Finance Corporation
This battery farm was the world’s largest when it was launched in 2017, but it has since been overtaken. It is owned and operated by Neoen and developed by stakeholders including Tesla and the South Australian Government.
Tesla built the Hornsdale Power Reserve from its lithium-ion units for A$90 million ($57 million). The 50 MW expansion was completed in 2020. The Hornsdale Power Reserve (HPR) provides essential grid-support services, stabilizing the South Australian electricity grid. This reduces reliance on gas-fired power to supply peak demand while supporting the integration of renewable energy sources.
Since 2017, this grid-scale batter has saved South Australian consumers over $180 million. In fact, this facility has been so successful that a 50MW/64.5MWh expansion was approved and came online in late 2020.

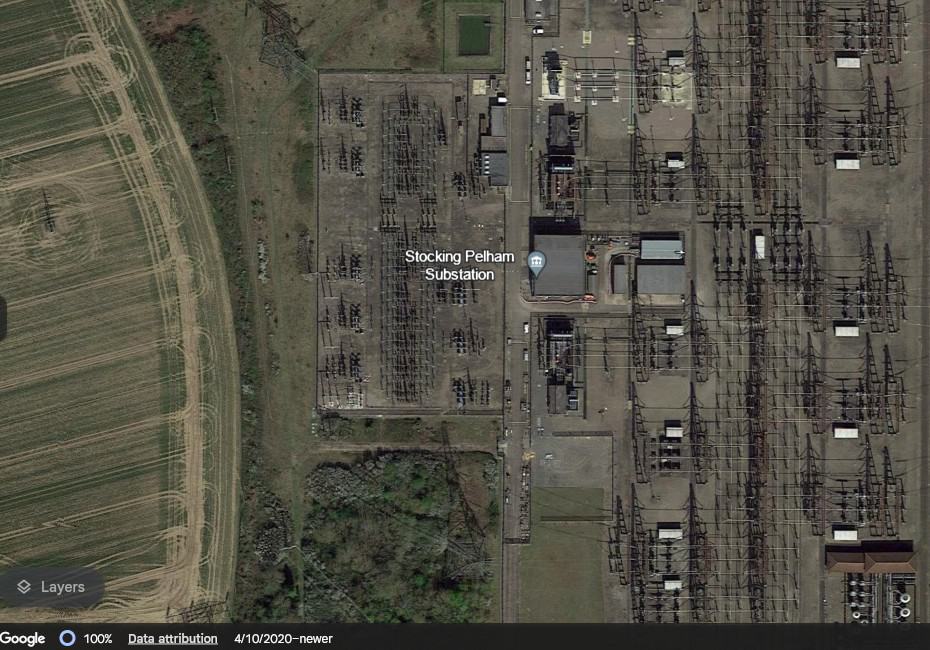
7. The Stocking Pelham Battery
- Location: Stocking Pelham, Hertfordshire, England, UK
- Capacity: 50 MW / 50 MWh
- Launched: 2018
- Developers/Stakeholders: British Solar Renewables, Sunbelt SMA, Ovenden Allworks, Statera Energy
The United Kingdom’s largest battery is installed at a facility in Stocking Pelham near Bishops Stortford in Hertfordshire, England. It came online in July 2018. The 4,500m2 battery farm, also known as Pelham BESS, was designed by British Solar Renewables and constructed by Ovenden Allworks. It has a capacity of 50 MW of power storage over 50 MWh.
The battery is made up of:
- Seven SMA E-houses installed on concrete foundations
- 150,000 lithium-ion battery cells
- Over 1 kilometer of underground cabling and earth nests
- 27 inverters
- An SMA Power Plant Controller
- Connectors to transfer power to and from a neighboring 400kV substation
The power held in the Pelham BESS is enough to power 13,000 British homes. The battery units use control logic to adapt to demand and help keep the power supply consistent.
8. The Buzen Substation BESS
- Location: Buzen, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan
- Capacity: 50 MW / 300 MWh
- Launched: 2016
- Developers/Stakeholders: Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Kyushu Electric Power Co.
The Buzen Substation BESS, designed and built by the Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, is the world’s largest sodium-sulfur battery energy-storage system. It is installed at the Buzen Substation in Buzen, Fukuoka Prefecture. It is connected to the local grid, which is owned and operated by Kyushu Electric Power Co.
The Buzen BESS has a 50 MW output and 300 MWh capacity and is comprised of 252 containers that each provide 200kW. The containers are double-stacked and arranged in 63 four-module units. The containers that house the battery span over 150,000 square feet (14,000 square meters). The battery modules are monitored and controlled using Mitsubushi’s BLEnDer RE battery SCADA system.
The energy storage capabilities of this sodium-sulfur battery site are similar to pumped hydro facilities. The facility helps to balance supply and demand on the local grid and supports the integration of renewable energy sources by ensuring the power frequency remains consistent.
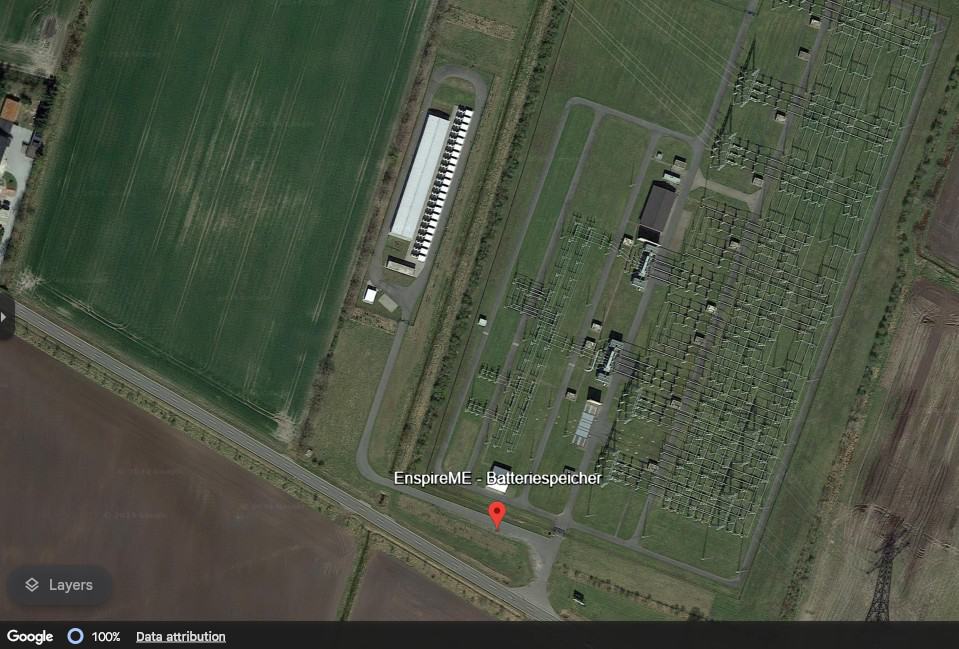
9. The EnspireME Battery
- Location: Jardelund, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
- Capacity: 48 MW
- Launched: 2018
- Developers/Stakeholders: Eneco Holding, Mitsubishi, NEC, NEC Energy Solutions
The EnspireME battery is one of Europe’s largest batteries in Jardelund in northern Germany. It has a 48 MW capacity and consists of 10,000 lithium-ion batteries. Mitsubishi Corporation designed this system in partnership with the Dutch energy supplier Eneco.
The battery has been operational since May 2018. It stores and supplies reserve capacity to the regional grid to help maintain a 50Hz frequency. The battery can provide power to 5,300 German homes. Eneco may also connect the battery to regional wind farms to store renewable energy.
The EnspireME battery is also strategically located to store energy for large onshore and offshore wind farms. The battery will likely play a role in reducing the blind capacity of renewable energy sources in the region. They can divert overproduction to the battery during particularly windy periods so the local grid does not become temporarily overloaded.
10. Notrees Energy Storage System
- Location: Notrees, Texas, United States
- Capacity: 36 MW
- Launched: 2012 (lead-acid), 2017 (lithium-ion deployment)
- Developers/Stakeholders: Duke Energy, Samsung SDI, ERCOT, US Department of Energy, Xtreme Power, Younicos
The Notrees Wind Farm Battery Energy Storage System is a 36 MW battery farm that has operated since 2012. They initially developed this battery energy storage complex using lead-acid battery technology but switched to lithium-ion in 2017.
A remote monitoring center is used to monitor the site using a proprietary energy storage management system to interpret signals from the grids and store or release power as required. The Notrees Energy Storage System connects to the ERCOT grid and helps to balance energy delivery on the network.
Duke Energy Renewables, a subsidiary of Duke Energy, is the primary owner of the Notrees Energy Storage System. The federal grants from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Electricity, provided over $21 million for upgrading the site to lithium-ion technology.
Duke Energy developed the battery farm in partnership with Xtreme Power for the lead-acid installation but now uses Samsung SDI battery technology installed by Younicos. The Samsung batteries come with a battery management system integrated into the site’s control center.

11. The Golden Valley Electric Battery
- Location: Fairbanks, Alaska, United States
- Capacity: 27 MW
- Launched: 2003
- Developers/Stakeholders: Golden Valley Electric, Saft, ABB, Incorp
The Golden Valley Electric Association BESS has a capacity of over 27 and serves the city of Fairbanks in Alaska. The battery was first commissioned in 2003 and uses nickel-cadmium technology. It comprises over 13,000 individual nickel-cadmium cells. Each cell is about the size of a desktop PC and has a lifespan of 30 years.
Golden Valley Electric Association owns this project and provides support to the local grid by supplying reserve capacity. The stored power can also stabilize the grid, providing more reliable service to customers. The association is currently considering upgrading the battery storage facility to lithium-ion technology as it is aging.
12. Ameresco Newmarket Battery Energy Storage System
- Location: Newmarket, Greater Toronto Area (GTA), Ontario, Canada
- Capacity: 4 MW / 16 MWh
- Launched: 2019
- Developers/Stakeholders: Ameresco, Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) Ontario, Tay Power Distribution Ltd, Tesla
Ameresco owns and operates this lithium-ion battery storage facility with Ontario’s Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) on a 10-year contract.
The total capacity of the site is 4 MW / 16 MWh. The battery went live in 2019 and feeds power into the Tay Power distribution grid to support critical timeshifting of energy consumption and production.
They built it using Tesla battery banks in 50-feet by 6-feet structures. Tesla remotely monitored the Tesla batteries in real-time in California. The entire facility cost $10.6 million. Stakeholders expect to achieve ROI by storing electricity during off-peak times and using the battery to stabilize the grid by using stored power during peak times.
This can offset or reduce reliance on burning gas or coal to meet peak power demand. Stakeholders expect this initial battery energy storage site to serve local consumers, but there is hope to expand the facility to serve the energy needs of hospitals and schools.
| Rank | Battery |
|---|---|
| #1 | The Edwards & Sanborn Solar Plus Storage Project |
| #2 | The Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility |
| #3 | The Dalian Flow Battery Energy Storage Peak-Shaving Power Station |
| #4 | Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E) Battery Energy Storage (BESS) Project |
| #5 | The Victorian Big Battery |
| #6 | The Hornsdale Power Reserve |
| #7 | The Stocking Pelham Battery |
| #8 | The Buzen Substation BESS |
| #9 | The EnspireME Battery |
| #10 | Notrees Energy Storage System |
| #11 | The Golden Valley Electric Battery |
| #12 | The Newmarket Battery Energy Storage System |
Want to Retire Early? Start Here (Sponsor)
Want retirement to come a few years earlier than you’d planned? Or are you ready to retire now, but want an extra set of eyes on your finances?
Now you can speak with up to 3 financial experts in your area for FREE. By simply clicking here you can begin to match with financial professionals who can help you build your plan to retire early. And the best part? The first conversation with them is free.
Click here to match with up to 3 financial pros who would be excited to help you make financial decisions.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©iStock.com/ArnyGFX.
