George Fowler was an American inventor who is famous for creating a slide bar adder, known as Fowler’s Adder. He was granted the first patent for his adding machine in 1863, and then a second one in 1890 for an improved version. Fowler’s Adder could be used to complete addition sums by inserting a pin or a pencil into the appropriate slots and sliding the numbers along. It then showed the result of the sum as figures on the underside of the slides (the device had to be turned upside down to see it).
Read on to explore the full history of George Fowler and his adding machine.
About George B. Fowler
On 14th July 1863, George B. Fowler of Chicago, Illinois, was granted his first patent (US39222) for an adding machine. In 1890 Fowler received a second patent (US432266) for an improved version of his device.
George B. Fowler was born in Long Island in 1834. In the early 1860s, he was a resident of Chicago, Illinois. By 1864 he had settled in New York City, opening a company to produce his adding device. In the late 1860s, he was a patent agent in Brooklyn.
Besides the above-mentioned patents for adders, Fowler went on to patent a variety of other devices, including a clothes and hat hook (US40923), a crusher and press (US136498), wood splitters (US53289), a game-box for ten-pins (US107030), a wagon-jack (US113285), an eggbeater and mixer (US256310), a picture cord and hook hanger (US357312), a cane and cigar case (US368823), a hand grip tester (US344095), a clam roaster (US424875), etc.
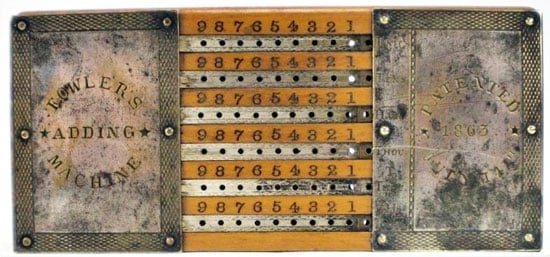
Fowler’s Adding Machine
In the 1860s the machine was advertised as the only practical and reliable adding machine in the world and was reported to be on the market since 1869, produced by the company of its inventor — Geo. B. Fowler & Co., Chicago, IL (see the upper photo).
Fowler garnered testimonials from lumber dealers, bookkeepers, and insurance companies, and hoped to find agents who would pay substantial sums to market his machine, but there is no indication that this occurred.
Later on, Fowler moved to New York and founded a new company — Fowler Adding Machine Co., New York, which produced the device. When launched to the market, the device cost $5. In the 1890s the device was sold for $8 by the Universal Adding Machine Co., under the name Universal Adding Machine.
How It Worked
The machine (see the lower drawing from the first patent) was a slide bar adder, operated by pin or pencil. It was a wood and metal device, with measurements of 1 cm x 22.5 cm x 11.5 cm.
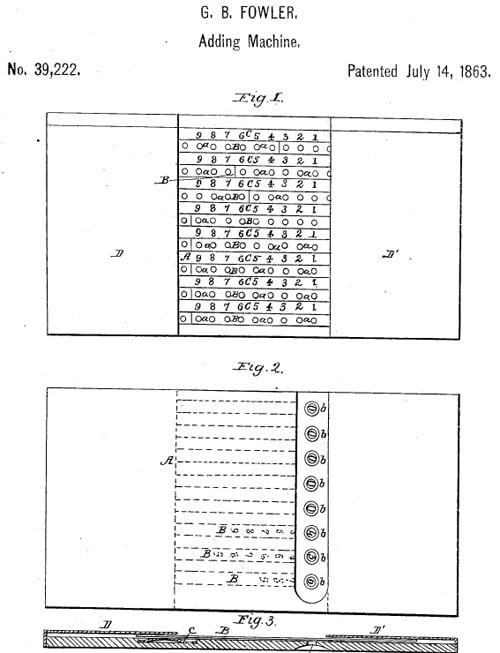
The upper slide represents the units, the next the tens, etc. If it is desired to add two numbers, for instance, 251 and 185, the pin is inserted into the hole opposite figure 1 on the first slide, and said slide is pushed toward the right until the pin strikes the cap D’. Then the pin is inserted into the hole opposite figure 5 on the second slide, and so on for all digits of the addends.
If the hole is on the dark portion of the slide, then the said slide has to be moved leftward, instead of rightward. The result of the operation is ascertained by turning the platform upside down and noticing the figures appearing on the underside of the slides opposite to the apertures (see the lower image) on the platform.

The image featured at the top of this post is ©Unknown author / public domain.